Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery for proximal femoral and other closed long bone fractures
- PMID: 20238310
- PMCID: PMC7043359
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000244.pub2
Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery for proximal femoral and other closed long bone fractures
Abstract
Background: Surgical site infection and other hospital-acquired infections cause significant morbidity after internal fixation of fractures. The administration of antibiotics may reduce the frequency of infections.
Objectives: To determine whether the prophylactic administration of antibiotics in people undergoing surgical management of hip or other closed long bone fractures reduces the incidence of surgical site and other hospital-acquired infections.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Bone, Joint and Muscle Trauma Group Specialised Register (December 2009), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library 2009, Issue 4), MEDLINE (1950 to November 2009), EMBASE (1988 to December 2009), other electronic databases including the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (December 2009), conferences proceedings and reference lists of articles.
Selection criteria: Randomised or quasi-randomised controlled trials comparing any regimen of systemic antibiotic prophylaxis administered at the time of surgery, compared with no prophylaxis, placebo, or a regimen of different duration, in people with a hip fracture undergoing surgery for internal fixation or prosthetic replacement, or with any closed long bone fracture undergoing internal fixation. All trials needed to report surgical site infection.
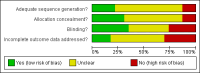
Data collection and analysis: Two authors independently screened papers for inclusion, assessed risk of bias and extracted data. Pooled data are presented graphically.
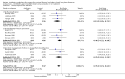
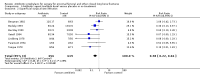
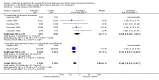
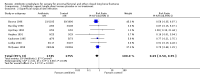
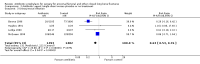
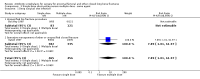
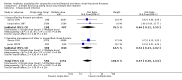
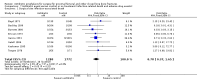
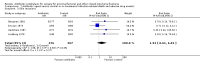
Main results: Data from 8447 participants in 23 studies were included in the analyses. In people undergoing surgery for closed fracture fixation, single dose antibiotic prophylaxis significantly reduced deep surgical site infection (risk ratio 0.40, 95% CI 0.24 to 0.67), superficial surgical site infections, urinary infections, and respiratory tract infections. Multiple dose prophylaxis had an effect of similar size on deep surgical site infection (risk ratio 0.35, 95% CI 0.19 to 0.62), but significant effects on urinary and respiratory infections were not confirmed. Although the risk of bias in many studies as reported was unclear, sensitivity analysis showed that removal from the meta-analyses of studies at high risk of bias did not alter the conclusions. Economic modelling using data from one large trial indicated that single dose prophylaxis with ceftriaxone is a cost-effective intervention. Data for the incidence of adverse effects were very limited, but as expected they appeared to be more common in those receiving antibiotics, compared with placebo or no prophylaxis.
Authors' conclusions: Antibiotic prophylaxis should be offered to those undergoing surgery for closed fracture fixation.
Conflict of interest statement
None known.
Figures
















Update of
-
Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery for proximal femoral and other closed long bone fractures.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD000244. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000244. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD000244. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000244.pub2. PMID: 11279687 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Bergman 1982 {published data only}
-
- Bergman BR. Antibiotic prophylaxis in open and closed fractures: a controlled clinical trial. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1982;53(1):57‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bodoky 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bodoky A, Neff U, Heberer M, Harder F. Antibiotic prophylaxis with two doses of cephalosporin in patients managed with internal fixation for a fracture of the hip. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1993;75(1):61‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Bodoky A, Neff U, Heberer M, Harder F. Preoperative assessment of at‐risk patients in traumatology [Praoperative erfassung von risikopatienten in der traumatologie]. Helvetica Chirurgica Acta 1989;56(1‐2):91‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boxma 1996 {published data only}
-
- Boxma H, Broekhuizen T, Patka P, Oosting H. Randomised controlled trial of single dose antibiotic prophylaxis in surgical treatment of closed fractures: the Dutch Trauma Trial. Lancet 1996;347(9009):1133‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Boyd 1973 {published data only}
-
- Boyd RJ, Burke JF, Colton T. A double‐blind clinical trial of prophylactic antibiotics in hip fractures. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1973;55(6):1251‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Buckley 1990 {published data only}
-
- Buckley R, Hughes GNF, Snodgrass T, Huchcroft SA. Perioperative cefazolin prophylaxis in hip fracture surgery. Canadian Journal of Surgery 1990;33(2):122‐5. [EMBASE: 1990261943] - PubMed
-
- Buckley RE, Hughes GNF. Perioperative cefazolin prophylaxis in hip fracture surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐British Volume 1989;71B:343. - PubMed
Burnett 1980 {published data only}
-
- Burnett JW, Gustilo RB, Williams DN, Kind AC. Prophylactic antibiotics in hip fracture. A double‐blind, prospective study. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1980;62:457‐62. - PubMed
Ericson 1973 {published data only}
-
- Ericson C, Lidgren L, Lindberg L. Cloxacillin in the prophylaxis of post‐operative infections of the hip. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1973;55:808‐43. - PubMed
Garcia 1991 {published data only}
-
- Garcia S, Lozana ML, Gatell JM, Soriana E, Ramon R, Sanmiguel JG. Prophylaxis against infection. Single‐dose cefonicid compared with multiple dose cefamandole. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1991;73(7):1044‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gatell 1984 {published data only}
-
- Gatell JM, Riba J, Lozana ML, Mana A, Ramon R, SanMiguel JG. Prophylactic cefamandole in orthopaedic surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1984;66(8):1219‐22. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gatell 1987 {published data only}
-
- Gatell JM, Garcia S, Lozano L, Soriano E, Ramon R, SanMiguel JG. Perioperative cefamandole prophylaxis against infections. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1987;69(8):1189‐93. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hedstrom 1987 {published data only}
-
- Hedstrom SA, Lidgren L, Sernbo I, Torholm C, Onnerfalt R. Cefuroxime prophylaxis in trochanteric hip fracture operations. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1987;58(4):361‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hjortrup 1990 {published data only}
-
- Hjortrup A, Sorensen C, Mejdahl S, Horsneas M, Kjersgaard P. Antibiotic prophylaxis in surgery for hip fractures. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1990;61(2):152‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Kjersgaard P, Hjortrup A, Moesgaard F, Horsnaes M. Preventive antibiotic treatment in hip fracture surgery [Profylaktiske antibiotika ved operation for hoftefraktur]. Ugeskrift for Laeger 1987;149(11):713‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hughes 1991 {published data only}
-
- Hughes SP, Miles RS, Littlejohn M, Brown E. Is antibiotic prophylaxis necessary for internal fixation of low‐energy fractures?. Injury 1991;22(2):111‐3. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jones 1987b {published data only}
-
- Jones RN, Wojeski W, Bakke J, Porter C, Searles M. Antibiotic prophylaxis of 1,036 patients undergoing elective surgical procedures. A prospective, randomized comparative trial of cefazolin, cefoxitin and cefotaxime in a prepaid medical practice. American Journal of Surgery 1987;153(4):341‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Karachalios 1987 {published data only}
-
- Karachalios T, Lyritis G, Hatzopoulos E, Sapkas G. Single dose prophylaxis of ceftriaxone versus standard dosage of cefotaxime in the prophylaxis of bacterial complications in orthopaedic surgery. Chemioterapia 1987;6(Suppl 2):573‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Karachalios T, Lyritis GP, Hatzopoulos E. Antibiotic prophylaxis in the surgical treatment of peritrochanteric fractures: a comparative trial between two cephalosporins. Chemotherapy 1990;36(6):448‐53. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kaukonen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Kaukonen JP, Kemppainen E, Makijarvi J, Touminen T. One dose cefuroxime prophylaxis in hip fracture surgery. Annales Chirurgica et Gynaecologiae 1995;84(4):417‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lindberg 1978 {published data only}
-
- Lindberg L, Tjörnstrand B. Prophylactic use of cephradine against postoperative infections of petrochanteric fractures. Archives of Orthopaedic & Traumatic Surgery 1978;92(2‐3):189‐90. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Luthje 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lüthje P, Nurmi I, Aho H, Honkanene P, Jokipii P, Kataja M, et al. Single dose antibiotic prophylaxis in osteosynthesis for hip fractures. A clinical multicentre study in Finland. Annales Chirurgiae at Gynaecologiae 2000;89(2):125‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
McQueen 1990 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- McQueen MM, Littlejohn MA, Miles RS, Hughes SPF. Antibiotic prophylaxis in proximal femoral fracture. Injury 1990;21(2):104‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nelson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Heydemann JS, Nelson CL. Short‐term preventive antibiotics. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research 1986;(205):184‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nelson CL, Green TG, Porter RA, Warren RD. One day versus seven days of preventive antibiotic therapy in orthopedic surgery. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research 1983;(176):258‐63. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nungu 1995 {published data only}
-
- Nungu KS, Larsson S, Wallinder L, Holm S. Bone and wound fluid concentrations of cephalosporins. Oral cefadroxil and parenteral cefuroxime compared in 52 patients with a trochanteric fracture. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1995;66(2):161‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Nungu KS, Olereud C, Rehnberg L, Larsson S, Nordell P, Allvin I, et al. Prophylaxis with oral cefadroxil versus intravenous cefuroxime in trochanteric fracture surgery. A clinical multicentre study. Archives of Orthopaedic & Trauma Surgery 1995;114(6):303‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Paiement 1994 {published data only}
-
- Paiement GD, Renaud E, Dagenais G, Gosselin RA. Double‐blind randomized prospective study of the efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis for open reduction and internal fixation of closed ankle fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 1994;8(1):64‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Tengve 1978 {published data only}
-
- Tengve B, Kjellander J. Antibiotic prophylaxis in operations on trochanteric femoral fractures. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1978;60(1):97‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Ali 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ali M, Raza A. Role of single dose antibiotic prophylaxis in clean orthopedic surgery. Journal of the College of Physicians & Surgeons ‐ Pakistan 2006;16(1):45‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Benson 1983 {published data only}
-
- Benson DR, Riggins RS, Lawrence RM, Hoeprich PD, Huston AC, Harrison JA. Treatment of open fractures: a prospective study. Journal of Trauma ‐ Injury Infection & Critical Care 1983;23(1):25‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Braun 1987 {published data only}
-
- Braun R, Enzler MA, Rittmann WW. A double‐blind clinical trial of prophylactic cloxacillin in open fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 1987;1(1):12‐7. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Centulio 1988 {published data only}
-
- Centulio F, Conticello A. Antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis with ceftriaxone in surgical implantation of a non‐cemented hip prosthesis: comparison of 2 dosage schemes. Chirurgia Degli Organi di Movimento 1988;73(4):357‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chiu 1993 {published data only}
-
- Chiu KY, Ng KH, Fung B, Lau SK, Chow SP. A prospective randomized study on four regimes of antibiotic prophylaxis for hip fracture operations. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ British Volume 1993;75B(Suppl 3):230.
Da Silva 1987 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Silva AD, Okumura AH, Pinho NM, Farcetta F, Chohfi M. Perioperative antibioticotherapy in the prevention of infection in bone surgery [Antibioticoterapia peroperatória na prevençäo da infecçäo em cirurgia óssea]. Revista Brasileira de Ortopedia 1987;22(1):23‐8.
De Benedictis 1984 {published data only}
-
- Benedictis KJ, Rowan NM, Boyer BL. A double‐blind study comparing cefonicid with cefazolin as prophylaxis in patients undergoing total hip or knee replacement. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1984;6(4):901‐4. - PubMed
Dellinger 1988 {published data only}
-
- Dellinger EP, Caplan ES, Weaver LD, Wertz MJ, Droppert BM, Hoyt N, et al. Duration of preventive antibiotic administration for open extremity fractures. Archives of Surgery 1988;123(3):333‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Evrard 1988 {published data only}
-
- Evrard J, Doyon F, Acar JF, Salord JC, Mazas F, Flamant R. Two day cefamandole versus five‐day cephazolin prophylaxis in 965 total hip replacements. Report of a multicentre double blind randomised trial. International Orthopaedics 1988;12(1):69‐73. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garotta 1991 {published data only}
-
- Garotta F, Pamparana F. Antimicrobial prophylaxis with ceftizoxime versus cefuroxime in orthopedic surgery. Ceftizoxime Orthopedic Surgery Italian Study Group. Journal of Chemotherapy. 1991;3(Suppl 2):34‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gunst 1984 {published data only}
-
- Gunst JP, Deletang S, Rogez JM, Blanloeil Y, Baron D, Dixneuf B. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy with cefamandole in total hip surgery replacement using Charnley's tent. A randomized study [Antibiotherapie prophylactique par le cefamandole dans la chirurgie de la prosthese totale de hanche sous tente de Charnley. Etude randomisee]. Pathologie Biologie 1984;32(5 Pt 2):567‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Henley 1986 {published data only}
-
- Henley MB, Jones RE, Wyatt RW, Hofmann A, Cohen RL. Prophylaxis with cefamandole nafate in elective orthopaedic surgery. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research 1986;(209):249‐54. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Hill 1981 {published data only}
-
- Hill C, Flamant R, Mazas F, Evrard J. Prophylactic cefazolin versus placebo in total hip replacement. Report of a multicentre double‐blind randomised trial. Lancet 1981;1(8224):795‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Johnson 1988 {published data only}
-
- Johnson KD, Bone LB, Scheinberg R. Severe open tibial fractures: a study protocol. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 1988;2(3):175‐80. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jones 1985 {published data only}
-
- Jones S, DiPiro JT, Nix DE, Bhatti NA. Cephalosporins for prophylaxis in operative repair of femoral fractures. Levels in serum, muscle, and hematoma. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1985;67(6):921‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jones 1987 {published data only}
-
- Jones RN, Wojeski WV. Single‐dose cephalosporin prophylaxis of 929 surgical procedures in a prepaid group practice: a prospective randomized comparison of cefoperazone and cefotaxime. Diagnostic Microbiology & Infectious Disease 1987;6(4):323‐34. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Knapp 1996 {published data only}
-
- Knapp TP, Patzakis MJ, Lee J, Seipel PR, Abdollahi K, Reisch RB. Comparison of intravenous and oral antibiotic therapy in the treatment of fractures caused by low‐velocity gunshots. A prospective, randomized study of infection rates. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1996;78(8):1167‐71. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Lidwell 1984 {published data only}
Liebergall 1995 {published data only}
-
- Liebergall M, Mosheiff R, Rand N, Peyser A, Shaul J, Kahane Y, et al. A double‐blinded, randomized, controlled clinical trial to compare cefazolin and cefonicid for antimicrobial prophylaxis in clean orthopedic surgery. Israel Journal of Medical Science 1995;31(1):62‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mauerhan 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mauerhan DR, Nelson CL, Smith DL, Fitzgerald RH Jr, Slama TG, Petty RW, et al. Prophylaxis against infection in total joint arthroplasty. One day of cefuroxime compared with three days of cefazolin. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1994;76(1):39‐45. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mollan 1994 {published data only}
-
- Mollan RAB, Haddock M, Webb CH. Teicoplanin vs cephamandole for antimicrobial prophylaxis in prosthetic joint implant surgery; preliminary results. European Journal of Surgery. Supplement 1992;(567):19‐21. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Patzakis 1977 {published data only}
-
- Patzakis MJ, Ivler D. Antibiotic and bacteriologic considerations in open fractures. Southern Medical Journal 1977;70(Suppl 1):46‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pavel 1974 {published data only}
-
- Pavel A, Smith RL, Ballard A, Larsen IJ. Prophylactic antibiotics in clean orthopaedic surgery. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery ‐ American Volume 1974;56(4):777‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
-
- Pavel A, Smith RL, Ballard A, Larson IJ. Prophylactic antibiotics in elective orthopedic surgery: a prospective study of 1,591 cases. Southern Medical Journal 1977;70(Suppl 1):50‐5. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Periti 1989 {published data only}
-
- Periti P, Jacchia E. Ceftriaxone as short‐term antimicrobial chemoprophylaxis in orthopedic surgery: a 1‐year multicenter follow‐up. Preliminary results of a controlled multicentre study. European Surgical Research 1989;21(Suppl 1):25‐32. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Periti 1992 {published data only}
-
- Periti P, Stringa G, Donati L, Mazzei T, Mini E, Novelli A. Teicoplanin‐ its role in systemic therapy of burns infections and as prophylaxis for orthopaedic surgery. Italian Study Groups for Antimicrobial Prophylaxis in Orthopaedic Surgery and Burns. European Journal of Surgery, Acta Chirurgica, Supplement 1992;(567):3‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pollard 1979 {published data only}
Schulitz 1980 {published data only}
-
- Schulitz KP, Winkellman W, Schoening B. The prophylactic use of antibiotics in alloarthroplasty of the hip joint for coxarthrosis. Archives of Orthopaedic & Traumatic Surgery 1980;96(2):79‐82. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vainionpaa 1988 {published data only}
-
- Vainionpaa S, Wilppula E, Lalla M, Renkonen OV, Rokkanen P. Cefamandole and isoxazolyl penicillins in antibiotic prophylaxis of patients undergoing total hip or knee‐joint arthroplasty. Archives of Orthopaedic & Traumatic Surgery 1988;107(4):228‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Van Meirhaeghe 1989 {published data only}
-
- Meirhaeghe J, Verdonk R, Vershraegen G, Myny P, Paeme G, Claessens H. Flucloxacillin compared with cefazolin in short‐term prophylaxis for clean orthopedic surgery. Archives of Orthopaedic & Trauma Surgery 1989;108(5):308‐13. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Visuri 1976 {published data only}
-
- Visuri T, Antila P, Laurent LE. A comparison of dicloxacillin and ampicillin in the antibiotic prophylaxis of total hip replacement. Annales Chirurgiae et Gynaecologiae 1976;65(1):58‐61. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wymenga 1992 {published data only}
-
- Wymenga A, Horn J, Theeuwes A, Muytjens H, Slooff T. Cefuroxime for prevention of post‐operative coxitis. One versus three doses tested in a randomized multicenter study of 2651 arthroplasties. Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica 1992;63(1):19‐24. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
ISRCTN75423827 {published data only}
-
- Davey P. Randomised trial of extended antibiotic prophylaxis for fracture fixation and joint replacement: clinical benefits versus ecological risks. http://isrctn.org/ISRCTN75423827. [ISRCTN75423827]
NCT00610987 {published data only}
-
- Greenberg DD, Anderson LK. Antibiotic prophylaxis in orthopaedic traumatology: a prospective, randomized trial of duration of administration. http://clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT00610987. [NCT00610987]
Additional references
Albers 1994
-
- Albers BA, Patka P, Haarman HJTM, Kostense PJ. Cost effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis for closed fractures [Kosteneffektivat einer Antibiotikaprophylaxe bei Senkung des Infectionsrisikos um 0,25%]. Unfallchirurgie 1994;97(12):625‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Burke 1961
-
- Burke JF. The effective period of preventive antibiotic action in experimental incisions and dermal lesions. Surgery 1961;50:161‐8. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Cranny 2008
-
- Cranny G, Elliott R, Weatherly H, Chambers D, Hawkins N, Myers L, et al. A systematic review and economic model of switching from non‐glycopeptide to glycopeptide antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery. Health Technology Assessment 2008;12(1):1‐168. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Doyon 1989
-
- Doyon F, Evrard J, Mazas F. Evaluation of therapeutic trials published apropos of antibiotic prophylaxis in orthopedic surgery [Evaluation des essais therapeutiques publies sur l'antibioprophylaxie en chirurgie orthopedique]. Revue de Chirurgie Orthopedique et Reparatrice de l Appareil Moteur. 1989;75(2):72‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Higgins 2009
-
- Higgins JPT, Altman DG. Chapter 8. Assessing risk of bias in included studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 [updated September 2009]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Lefebvre 2009
-
- Lefebvre C, Manheimer E, Glanville J. Chapter 6: Searching for studies. In: Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.0.2 (updated September 2009). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2009. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Levy 2002
-
- Levy SB. The 2000 Garrod lecture. Factors impacting on the problem of antibiotic resistance. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 2002;49(1):25‐30. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Moher 2001
-
- Moher D, Schulz KF, Altman DG, CONSORT GROUP. The CONSORT statement: revised recommendations for improving the quality of reports of parallel group randomized trials. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001;134(8):657‐62. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Norden 1991
-
- Norden CW. Antibiotic prophylaxis in orthopaedic surgery. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1991;13(Suppl 10):842‐6. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Platt 1991
-
- Platt R. Methodological aspects of clinical studies of perioperative antibiotic prophylaxis. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1991;13(Suppl 10):810‐4. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Roberts 2009
-
- Roberts RR, Hota B, Ahmad I, Scott RD 2nd, Foster SD, Abbasi F, et al. Hospital and societal costs of antimicrobial‐resistant infections in a Chicago teaching hospital:implications for antibiotic stewardship.. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2009;49(8):1175‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Slobogean 2008
-
- Slobogean GP, Kennedy SA, Davidson D, O'Brien PJ. Single‐ versus multiple‐dose antibiotic prophylaxis in the surgical treatment of closed fractures: a meta‐analysis. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma 2008;22(4):264‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Southwell‐Keely 2004
-
- Southwell‐Keely JP, Russo RR, March L, Cumming R, Cameron I, Brnabic AJ. Antibiotic prophylaxis in hip fracture surgery: a metaanalysis. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research 2004;(419):179‐84. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

