Non-surgical interventions for eosinophilic esophagitis
- PMID: 20238328
- PMCID: PMC7173717
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004065.pub3
Non-surgical interventions for eosinophilic esophagitis
Update in
-
Medical treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 20;7(7):CD004065. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004065.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37470293 Free PMC article. Review.
Abstract
Background: People with eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) have clinical symptoms of esophageal disease, an elevated intraepithelial eosinophil count (15 in one or more high power field at endoscopy), consistent endoscopic findings and failure to respond to gastric acid suppressants. The cause of EE is unknown, however dietary, environmental and immunological factors may contribute. Current medical therapies include steroids, dietary manipulation, mast cell inhibitors, leukotriene receptor antagonists and immune modulators; however there is no universal approach to treatment.
Objectives: To evaluate the benefits and harms of medical interventions for EE.
Search strategy: We searched the Cochrane Upper Gastrointestinal and Pancreatic Diseases Group trials register (The Cochrane Library Issue 1, 2009), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (The Cochrane Library Issue 1, 2009), MEDLINE (1966 to February 2009) and EMBASE (1980 to February 2009).
Selection criteria: Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing a medical or dietary intervention for EE with a placebo or with another medical intervention.
Data collection and analysis: Two reviewers independently screened the titles of abstracts.
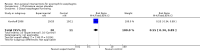
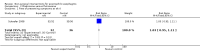
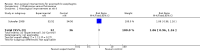
Main results: Three RCTs fulfilled inclusion criteria, two in children and one in adults. In one trial, topical fluticasone decreased vomiting more than placebo (67% versus (vs) 27%, P<0.05) but did not improve dysphagia. Histological remission was reported in fluticasone group compared with placebo group (50% vs 9%, P=0.05; RR 5.5, 95%CI 0.81 to 37.49). One recipient of fluticasone developed oral candidiasis. In trial comparing fluticasone with oral prednisone, symptom resolution and improvement of esophagitis were similar. Majority of participants were symptom free at four weeks with no difference between groups (RR 1.03, 95%CI 0.95 to 1.11). Symptom relapse usually occurred within six weeks of stopping therapy and 45% had symptom relapse at six month follow-up with no difference between groups. With prednisone, 40% suffered adverse effects and three withdrew early from treatment with severe adverse effects (hyperphagia, weight gain, cushingoid features). With fluticasone, 15% developed esophageal candidiasis and 45% had relapse in symptoms at week 24. Histological improvement occurred in majority at four weeks with no difference between groups. In the third trial comparing mepolizumab to placebo, there was no difference in symptom response with mepolizumab compared to placebo, but decrease in esophageal eosinophil count was greater with mepolizumab than placebo (67% vs 25%).
Authors' conclusions: As only three relevant RCTs were identified, we have limited capacity to compare the benefits and harms of medical interventions currently used for treating EE. Further RCTs on therapies for EE are required.
Conflict of interest statement
None known
Figures


Update of
-
Non-surgical interventions for eosinophilic oesophagitis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004;(3):CD004065. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004065.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Mar 17;(3):CD004065. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD004065.pub3. PMID: 15266514 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
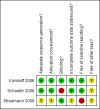
Konikoff 2006 {published data only}
-
- Konikoff MR, Noel RJ, Blanchard C, et al. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial of fluticasone propionate for pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis. Gastroenterology 2006;131:1381‐91. - PubMed
Schaefer 2008 {published data only}
-
- Gupta SK, Fitzgerald JF, Davis MM, Croffie JM, et al. Treatment of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis (AEE) with oral prednisone (P) and swallowed fluticasone (F): a randomized, prospective study in children. Gastroenterology. 2003; Vol. 124(4suppl 1):A‐19.
-
- Schaefer ET, Fitzgerald JF, Molleston JP, Croffie JM, Pfefferkorn MD, et al. Comparison of Oral Prednisone and Topical Fluticasone in the Treatment of Eosinophilic Esophagitis: a Randomized Trial in Children. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2008;6:165‐73. - PubMed
Straumann 2008 {published data only}
-
- Straumann A, Conus H, Kita G, Kephart C, Bussmann C, Beglinger J, et al. Mepolizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody to IL‐5, for severe eosinophilic esophagitis in adults: a randomized, placebo‐controlled double‐blind trial. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2008;121(2, Supplement 1):S44.
References to studies excluded from this review
Helou 2008 {published data only}
-
- Helou EF, Simonson J, Arora AS. 3‐yr‐follow‐up of topical corticosteroid treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2008;9:2194‐9. - PubMed
Kagalwalla 2006 {published data only}
-
- Kagalwalla AF, Sentongo TA, Ritz S, Hess T, Nelson SP, et al. Effect of six‐food elimination diet on clinical and histologic outcomes in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2006;4:1097‐102. - PubMed
Spergel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Spergel JM, Beausoleil JL, Mascarenhas M, Liacouras CA. The use of skin prick tests and patch tests to identify causative foods in eosinophilic esophagitis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2002;109:363‐8. - PubMed
Spergel 2005 {published data only}
-
- Spergel JM, Andrews T, Brown‐Whitehorn TF, Beausoleil JL, Liacouras CA. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with specific food elimination diet directed by a combination of skin prick and patch tests. Annals of Allergy Asthma and Immunology 2005;95:336‐43. - PubMed
Additional references
Assa'ad 2007
-
- Assa'ad AH, Putnam PE Collins MH, et al. Pediatric patients with eosinophilic esophagitis: an 8‐year follow‐up. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2007;119:731‐8. - PubMed
Attwood 2003
Bohm 2008
-
- Bohm M, Richter JE. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis: overview, current limitations, and future direction. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2008;103:2635‐44. - PubMed
Croese 2003
-
- Croese J, Fairley SK, Masson JW, et al. Clinical and endoscopic features of eosinophilic esophagitis in adults. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy 2003;58:516‐22. - PubMed
Faubion 1998
-
- Faubion WA, Jr, Perrault J, Burgart LJ, Zein NN, Clawson M, Freese DK. Treatment of eosinophilic esophagitis with inhaled corticosteroids. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1998;27(1):90‐3. - PubMed
Furuta 2007
-
- Furuta GT, Liacouras CA, Collins MH, et al. First International Gastrointestinal Eosinophil Research Symposium (FIGERS). Gastroenterology 2007;133:1342‐63. - PubMed
Gupta 2003
-
- Gupta SK, Fitzgerald JF, Davis MM, Croffie JM, et al. Treatment of allergic eosinophilic esophagitis (AEE) with oral prednisone (P) and swallowed fluticasone (F): a randomized, prospective study in children. Gastroenterology. 2003; Vol. 124(4suppl 1):A‐19.
Hassall 1996
-
- Hassall E. Macroscopic versus microscopic diagnosis of reflux esophagitis: erosions or eosinophils?. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1996;22(3):321‐5. - PubMed
Higgins 2008
-
- Higgins JP. Commentary: Heterogeneity in meta‐analysis should be expected and appropriately quantified. International Journal of Epidemiology 2008;37:1158‐60. - PubMed
Kelly 1995
-
- Kelly KJ, Lazenby AJ, Rowe PC, Yardley JH, Perman JA, Sampson HA. Eosinophilic esophagitis attributed to gastroesophageal reflux: improvement with an amino acid‐based formula. Gastroenterology 1995;109(5):1503‐12. - PubMed
Khan 2003
-
- Khan S, Orenstein SR, Lorrenzo C, Kocoshis SA, Putnam PE, Sigurdsson L, et al. Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Strictures, Impaction, Dysphagia. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 2003;48(1):22‐9. - PubMed
Liacouras 1998
-
- Liacouras CA, Wenner WJ, Brown K, Ruchelli E. Primary eosinophilic esophagitis in children: successful treatment with oral corticosteroids. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition 1998;26(4):380‐5. - PubMed
Markowitz 2003
-
- Markowitz JE, Spergel JM, Ruchelli E, Liacouras CA. Elemental diet is an effective treatment for eosinophilic esophagitis in children and adolescents. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2003;98(4):777‐82. - PubMed
Mishra 2001
Orenstein 2000
-
- Orenstein SR, Shalaby TM, Lorenzo C, Putnam PE, Sigurdsson L, Kocoshis SA. The spectrum of pediatric eosinophilic esophagitis beyond infancy: a clinical series of 30 children. American Journal of Gastroenterology 2000;95(6):1422‐30. - PubMed
Perez‐Millan 1997
-
- Perez‐Millan A, Martin‐Lorente JL, Lopez‐Morante A, Yugero L, Saez‐Royuela F. Subserosal eosinophilic gastroenteritis treated efficaciously with sodium cromoglycate. Digestive diseases and sciences 1997;42(2):342‐4. - PubMed
Stone 2008
Teitelbaum 2002
-
- Teitelbaum JE, Fox VL, Twarog FJ, Nurko S, Antonilli D, Gleich G, et al. Eosinophilic oesophagitis in Children: Immunopathological analysis and response to fluticasone proprionate. Gastroenterology 2002;122(5):1216‐25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

