Alcohol, nutrition and liver cancer: role of Toll-like receptor signaling
- PMID: 20238401
- PMCID: PMC2842526
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1344
Alcohol, nutrition and liver cancer: role of Toll-like receptor signaling
Abstract
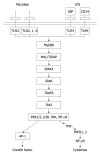
This article reviews the evidence that ties the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to the natural immune pro-inflammatory response to chronic liver disease, with a focus on the role of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling as the mechanism of liver stem cell/progenitor transformation to HCC. Two exemplary models of this phenomenon are reviewed in detail. One model applies chronic ethanol/lipopolysaccharide feeding to the activated TLR4 signaling pathway. The other applies chronic feeding of a carcinogenic drug, in which TLR2 and 4 signaling pathways are activated. In the drug-induced model, two major methyl donors, S-adenosylmethionine and betaine, prevent the upregulation of the TLR signaling pathways and abrogate the stem cell/progenitor proliferation response when fed with the carcinogenic drug. This observation supports a nutritional approach to liver cancer prevention and treatment. The observation that upregulation of the TLR signaling pathways leads to liver tumor formation gives evidence to the popular concept that the chronic pro-inflammatory response is an important mechanism of liver oncogenesis. It provides a nutritional approach, which could prevent HCC from developing in many chronic liver diseases.
2010 Baishideng. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
S-adenosylmethionine prevents the up regulation of Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling caused by chronic ethanol feeding in rats.Exp Mol Pathol. 2011 Jun;90(3):239-43. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Jan 25. Exp Mol Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21276439 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol and liver cancer.Alcohol. 2005 Apr;35(3):195-203. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2005.04.004. Alcohol. 2005. PMID: 16054981 Review.
-
Toll-like receptor 4 activity protects against hepatocellular tumorigenesis and progression by regulating expression of DNA repair protein Ku70 in mice.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1869-81. doi: 10.1002/hep.26234. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299825
-
Impact of the Innate Immune Response in the Actions of Ethanol on the Central Nervous System.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 Nov;40(11):2260-2270. doi: 10.1111/acer.13208. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27650785 Review.
-
Hepatitis C virus and alcohol: same mitotic targets but different signaling pathways.J Hepatol. 2011 May;54(5):956-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.08.016. Epub 2010 Dec 22. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21145809
Cited by
-
Toll-like receptors in the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease.Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2010;2010:710381. doi: 10.1155/2010/710381. Epub 2010 Aug 17. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2010. PMID: 20827314 Free PMC article.
-
Immunobiology of hepatocellular carcinoma.Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012 Jun;397(5):673-80. doi: 10.1007/s00423-011-0783-x. Epub 2011 Apr 9. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2012. PMID: 21479622 Review.
-
Role of cytokines and chemokines in alcohol-induced tumor promotion.Onco Targets Ther. 2017 Mar 17;10:1665-1671. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S129781. eCollection 2017. Onco Targets Ther. 2017. PMID: 28360527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alcohol and liver, 2010.World J Gastroenterol. 2010 Mar 21;16(11):1303. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v16.i11.1303. World J Gastroenterol. 2010. PMID: 20238395 Free PMC article.
-
Tollip promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via PI3K/AKT pathway.Open Med (Wars). 2022 Apr 1;17(1):626-637. doi: 10.1515/med-2022-0453. eCollection 2022. Open Med (Wars). 2022. PMID: 35434373 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hassan MM, Hwang LY, Hatten CJ, Swaim M, Li D, Abbruzzese JL, Beasley P, Patt YZ. Risk factors for hepatocellular carcinoma: synergism of alcohol with viral hepatitis and diabetes mellitus. Hepatology. 2002;36:1206–1213. - PubMed
-
- Britton RS, Bacon BR. Hereditary hemochromatosis and alcohol: a fibrogenic cocktail. Gastroenterology. 2002;122:563–565. - PubMed
-
- Kage M, Kage M, Liew CT, Xu Y, Peters RL. Alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiency in adults. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1986;36:1139–1148. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

