Slit3 inhibits Robo3-induced invasion of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 20298552
- PMCID: PMC2888193
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2955
Slit3 inhibits Robo3-induced invasion of synovial fibroblasts in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Introduction: The repellent factor family of Slit molecules has been described to have repulsive function in the developing nervous system on growing axons expressing the Robo receptors. However, until today no data are available on whether these repellent factors are involved in the regulation of synovial fibroblast (SF) activity in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods: mRNA expression in primary synovial fibroblasts was quantified by quantitative reverse transcription PCR and protein expression was measured by fluorescence activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. Different functional assays were performed with rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts (RASF): proliferation, migration and a novel in-vitro cartilage destruction assay.
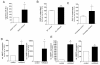
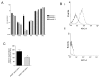
Results: First, we found increased expression of Robo3 expression in RASF compared to normal SF. Interestingly, analysis of data from a recently published genome-wide association study suggests a contribution of ROBO3 gene polymorphisms to susceptibility of RA. Functional assays performed with RASF revealed induction of migration and cartilage destruction by Robo3 and increased matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)1 and MMP3 expression. Treatment of RASF in early passages with Slit3 led to inhibition of migration whereas RASF in later passages, having reduced Robo3 expression in cell culture, were not inhibited by Slit3 treatment. Here, reduction of Robo3 expression from passage 3 to 10 might reflect an important step in losing repulsive activity of Slit3.
Conclusions: Taken together, our data showed that deregulation of the Robo3 receptor in synovial fibroblasts in RA correlates with aggressiveness of the fibroblasts. Slit3 reduces the migratory activity of synovial cells from patients with RA, potentially by repulsion of the cells in analogy to the neuronal system. Further studies will be necessary to prove Slit activity in vivo.
Figures
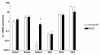

Similar articles
-
Expression of sentrin, a novel antiapoptotic molecule, at sites of synovial invasion in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):599-607. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(200003)43:3<599::AID-ANR17>3.0.CO;2-T. Arthritis Rheum. 2000. PMID: 10728754
-
Cartilage destruction mediated by synovial fibroblasts does not depend on proliferation in rheumatoid arthritis.Am J Pathol. 2003 May;162(5):1549-57. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64289-7. Am J Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12707039 Free PMC article.
-
FLICE-inhibitory protein expression in synovial fibroblasts and at sites of cartilage and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Rheum. 2002 Jun;46(6):1512-8. doi: 10.1002/art.10309. Arthritis Rheum. 2002. PMID: 12115181
-
Rheumatoid arthritis progression mediated by activated synovial fibroblasts.Trends Mol Med. 2010 Oct;16(10):458-68. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2010.07.004. Epub 2010 Aug 24. Trends Mol Med. 2010. PMID: 20739221 Review.
-
[Rheumatoid arthritis: new developments in the pathogenesis with special reference to synovial fibroblasts].Z Rheumatol. 2001 Oct;60(5):309-18. doi: 10.1007/s003930170030. Z Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11759230 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Robo3A and Robo3B expression is regulated via alternative promoters and mRNA stability.Cancer Cell Int. 2016 Sep 20;16:71. doi: 10.1186/s12935-016-0347-9. eCollection 2016. Cancer Cell Int. 2016. PMID: 27660555 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of microRNA-188-5p in activated rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 May 1;8(5):4953-62. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26191188 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and function of microRNA-188-5p in activated rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Jun 1;8(6):6607-16. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. Retraction in: Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Nov 01;8(11):15497. PMID: 26261542 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Peripheral neuronal sensitization and neurovascular remodelling in osteoarthritis pain.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025 Sep;21(9):526-545. doi: 10.1038/s41584-025-01280-3. Epub 2025 Aug 12. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2025. PMID: 40796685 Review.
-
SLIT3 deficiency attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac fibrosis and remodeling.JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 18;5(12):e136852. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.136852. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32644051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

