Amelogenesis imperfecta due to a mutation of the enamelin gene: clinical case with genotype-phenotype correlations
- PMID: 20298654
- PMCID: PMC2842984
Amelogenesis imperfecta due to a mutation of the enamelin gene: clinical case with genotype-phenotype correlations
Abstract
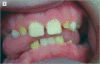
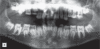
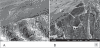
The major protein components of the enamel matrix include the most abundant amelogenin proteins as well as less plentiful proteins such as enamelin and ameloblastin. The enamel defect in amelogenesis imperfecta (Al) generally results in enamel that is too thin (hypoplastic) or too soft (hypocalcification or hypomaturation). Previous reports indicate that mutations in the human enamelin gene (ENAM) cause hypoplastic Al through autosomal-dominant inheritance patterns and patients may also exhibit an anterior open bite. Although crown resorption of unerupted teeth occurs more frequently in Al patients, this finding has not been previously associated with known ENAM mutations. The purpose of this article was to report the genotype-phenotype correlations for a 9-year, 11-month-old boy with a homozygous ENAM mutation (c.1258_1259insAG).
Figures


Similar articles
-
A mutation in the enamelin gene in a mouse model.J Dent Res. 2007 Aug;86(8):764-8. doi: 10.1177/154405910708600815. J Dent Res. 2007. PMID: 17652207
-
A nonsense mutation in the enamelin gene causes local hypoplastic autosomal dominant amelogenesis imperfecta (AIH2).Hum Mol Genet. 2002 May 1;11(9):1069-74. doi: 10.1093/hmg/11.9.1069. Hum Mol Genet. 2002. PMID: 11978766
-
Enamelin/ameloblastin gene polymorphisms in autosomal amelogenesis imperfecta among Syrian families.J Investig Clin Dent. 2011 Feb;2(1):16-22. doi: 10.1111/j.2041-1626.2010.00038.x. Epub 2010 Nov 8. J Investig Clin Dent. 2011. PMID: 25427323
-
Enamelin and autosomal-dominant amelogenesis imperfecta.Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14(6):387-98. doi: 10.1177/154411130301400602. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003. PMID: 14656895 Review.
-
Genes and related proteins involved in amelogenesis imperfecta.J Dent Res. 2005 Dec;84(12):1117-26. doi: 10.1177/154405910508401206. J Dent Res. 2005. PMID: 16304440 Review.
Cited by
-
ENAM mutations and digenic inheritance.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Oct;7(10):e00928. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.928. Epub 2019 Sep 2. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31478359 Free PMC article.
-
Amelogenesis imperfecta and anterior open bite: Etiological, classification, clinical and management interrelationships.J Orthod Sci. 2014 Jan;3(1):1-6. doi: 10.4103/2278-0203.127547. J Orthod Sci. 2014. PMID: 24987656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bodyweight assessment of enamelin null mice.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:246861. doi: 10.1155/2013/246861. Epub 2012 Dec 26. Biomed Res Int. 2013. PMID: 23509695 Free PMC article.
-
Amelogenin in Enamel Tissue Engineering.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;881:237-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22345-2_13. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26545753 Free PMC article.
-
Amelogenesis imperfecta and screening of mutation in amelogenin gene.Case Rep Dent. 2014;2014:319680. doi: 10.1155/2014/319680. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Case Rep Dent. 2014. PMID: 25045544 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robinson C, Brookes SJ, Shore RC, Kirkham J. The developing enamel matrix: Nature and function. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998;106(suppl 1):282–91. - PubMed
-
- Simmer JP, Hu JC. Dental enamel formation and its impact on clinical dentistry. J Dent Educ. 2001;65:896–905. - PubMed
-
- Hu JC, Yamakoshi Y. Enamelin and autosomal-dominant amelogenesis imperfecta. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:387–98. - PubMed
-
- Witkop CJ, SJ . Heritable defects of enamel. In: Stewart RE RE, Prescott GH, editors. Oral Facial Genetics. Mosby; St. Louis, Mo: 1976. pp. 151–226.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

