Neural heterogeneities and stimulus properties affect burst coding in vivo
- PMID: 20298764
- PMCID: PMC4529318
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.03.012
Neural heterogeneities and stimulus properties affect burst coding in vivo
Abstract
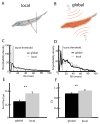
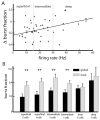
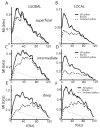
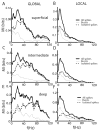
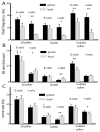
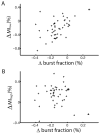
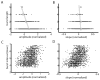
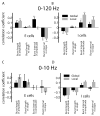
Many neurons tend to fire clusters of action potentials called bursts followed by quiescence in response to sensory input. While the mechanisms that underlie burst firing are generally well understood in vitro, the functional role of these bursts in generating behavioral responses to sensory input in vivo are less clear. Pyramidal cells within the electrosensory lateral line lobe (ELL) of weakly electric fish offer an attractive model system for studying the coding properties of burst firing, because the anatomy and physiology of the electrosensory circuitry are well understood, and the burst mechanism of ELL pyramidal cells has been thoroughly characterized in vitro. We investigated the coding properties of bursts generated by these cells in vivo in response to mimics of behaviorally relevant sensory input. We found that heterogeneities within the pyramidal cell population had quantitative but not qualitative effects on burst coding for the low frequency components of broadband time varying input. Moreover, spatially localized stimuli mimicking, for example, prey tended to elicit more bursts than spatially global stimuli mimicking conspecific-related stimuli. We also found small but significant correlations between burst attributes such as the number of spikes per burst or the interspike interval during the burst and stimulus attributes such as stimulus amplitude or slope. These correlations were much weaker in magnitude than those observed in vitro. More surprisingly, our results show that correlations between burst and stimulus attributes actually decreased in magnitude when we used low frequency stimuli that are expected to promote burst firing. We propose that this discrepancy is attributable to differences between ELL pyramidal cell burst firing under in vivo and in vitro conditions.
2010 IBRO. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bannister NJ, Larkman AU. Dendritic morphology of CA1 pyramidal neurones from the rat hippocampus: I. branching patterns. J Comp Neurol. 1995a;360:150–160. - PubMed
-
- Bannister NJ, Larkman AU. Dendritic morphology of CA1 pyramidal neurones from the rat hippocampus: II. spine distributions. J Comp Neurol. 1995b;360:161–171. - PubMed
-
- Bastian J, Chacron MJ, Maler L. Plastic and non-plastic cells perform unique roles in a network capable of adaptive redundancy reduction. Neuron. 2004;41:767–779. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

