Genetic variation at a single locus and age of onset for Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 20298972
- PMCID: PMC2874876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jalz.2010.01.011
Genetic variation at a single locus and age of onset for Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
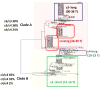
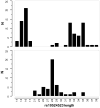
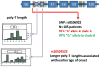
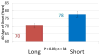
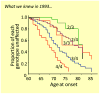
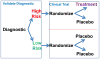
This perspective article provides an opportunity to explain a new genetic finding for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). It is specifically written for physicians and scientists who are interested in LOAD, but it may be relevant to those interested in identifying susceptibility variants for other complex diseases. The significant finding discussed here is that a variable-length, deoxythymidine homopolymer (poly-T) within intron 6 of the TOMM40 gene is associated with the age of onset of LOAD [Roses AD, Lutz MW, Amrine-Madsen H, Saunders AM, Crenshaw DG, Sundseth SS, et al. A TOMM40 variable-length polymorphism predicts the age of late-onset Alzheimer's disease. Pharmacogenomics J 2009 December 22;[Epublication ahead of print]. This result was obtained with a phylogenetic study of the genetic polymorphisms that reside within the linkage disequilibrium (LD) block that contains the TOMM40, APOE, and APOC1 genes from patients with LOAD and age-matched subjects without disease. Although the data will have diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic strategy implications, this perspective is meant to place the inheritance pattern for this "complex" human disease into context, and to highlight the potential utility of applying phylogenetic tools to the study of the genetics of complex diseases.
2010 The Alzheimer's Association. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Dr. Roses is the President of three companies filed as S-Corporations in the state of North Carolina: Cabernet Pharmaceuticals, Inc is a pipeline pharmacogenetic consultation and project management company that has other pharmaceutical companies as clients; Shiraz Pharmaceuticals, Inc. is focused on the commercialization of diagnostics, including companion diagnostics, for universities, pharmaceutical companies, and biotechnology companies; Zinfandel Pharmaceuticals is the sponsor of OPAL [Opportunity to Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease] which is a combined clinical validation of a diagnostic and a pharmacogenetic-assisted delay of onset clinical trial.
These companies are independent of Duke University but any intellectual property generated by Dr. Roses or his team is intended to be treated as Deane Drug Discovery Institute property once there is an established commercial value.
Figures
References
-
- Corder EH, Saunders AM, Strittmatter WJ, Schmechel DE, Gaskell PC, Small GW, Roses AD, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science. 1993;261:921–3. - PubMed
-
- Khoury MJ, Bertram L, Boffetta P, Butterworth AS, Chanock SJ, Dolan SM, Fortier I, Garcia-Closas M, Gwinn M, Higgins JP, et al. Genome-wide association studies, field synopses, and the development of the knowledge base on genetic variation and human diseases. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170:269–79. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

