Re-valuing the amygdala
- PMID: 20299204
- PMCID: PMC2862774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.02.007
Re-valuing the amygdala
Abstract
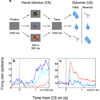
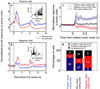
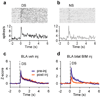
Recent advances indicate that the amygdala represents valence: a general appetitive/aversive affective characteristic that bears similarity to the neuroeconomic concept of value. Neurophysiological studies show that individual amygdala neurons respond differentially to a range of stimuli with positive or negative affective significance. Meanwhile, increasingly specific lesion/inactivation studies reveal that the amygdala is necessary for processes--for example, fear extinction and reinforcer devaluation--that involve updating representations of value. Furthermore, recent neuroimaging studies suggest that the human amygdala mediates performance on many reward-based decision-making tasks. The encoding of affective significance by the amygdala might be best described as a representation of state value-a representation that is useful for coordinating physiological, behavioral, and cognitive responses in an affective/emotional context.
(c) 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
From affective value to decision-making in the prefrontal cortex.Eur J Neurosci. 2008 Nov;28(9):1930-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2008.06489.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18973606
-
Emotion, cognition, and mental state representation in amygdala and prefrontal cortex.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010;33:173-202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.051508.135256. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20331363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional disconnection of the orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala impairs acquisition of a rat gambling task and disrupts animals' ability to alter decision-making behavior after reinforcer devaluation.J Neurosci. 2013 Apr 10;33(15):6434-43. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3971-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23575841 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the amygdala in decision-making.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003 Apr;985:356-69. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2003.tb07094.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2003. PMID: 12724171 Review.
-
The amygdala, reward and emotion.Trends Cogn Sci. 2007 Nov;11(11):489-97. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2007.08.013. Epub 2007 Nov 7. Trends Cogn Sci. 2007. PMID: 17988930 Review.
Cited by
-
Input-specific contributions to valence processing in the amygdala.Learn Mem. 2016 Sep 15;23(10):534-43. doi: 10.1101/lm.037887.114. Print 2016 Oct. Learn Mem. 2016. PMID: 27634144 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of serotonin on fear learning.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e42397. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042397. Epub 2012 Aug 3. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22879964 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The role of the amygdala in processing social and affective touch.Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2022 Feb;43:46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2021.08.004. Epub 2021 Sep 1. Curr Opin Behav Sci. 2022. PMID: 35602667 Free PMC article.
-
Desirability, availability, credit assignment, category learning, and attention: Cognitive-emotional and working memory dynamics of orbitofrontal, ventrolateral, and dorsolateral prefrontal cortices.Brain Neurosci Adv. 2018 May 8;2:2398212818772179. doi: 10.1177/2398212818772179. eCollection 2018 Jan-Dec. Brain Neurosci Adv. 2018. PMID: 32166139 Free PMC article.
-
Neurobiological correlates of violence perception in martial artists.Brain Behav. 2019 May;9(5):e01276. doi: 10.1002/brb3.1276. Epub 2019 Mar 24. Brain Behav. 2019. PMID: 30907076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pare D, Quirk GJ, Ledoux JE. New vistas on amygdala networks in conditioned fear. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2004;92:1–9. - PubMed
-
- LeDoux JE. Emotion circuits in the brain. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 2000;23:155–184. - PubMed
-
- Quirk GJ, Repa C, LeDoux JE. Fear conditioning enhances short-latency auditory responses of lateral amygdala neurons: parallel recordings in the freely behaving rat. Neuron. 1995;15:1029–1039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

