Self inhibition of phagocytosis: the affinity of 'marker of self' CD47 for SIRPalpha dictates potency of inhibition but only at low expression levels
- PMID: 20299253
- PMCID: PMC2878922
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2010.02.016
Self inhibition of phagocytosis: the affinity of 'marker of self' CD47 for SIRPalpha dictates potency of inhibition but only at low expression levels
Abstract
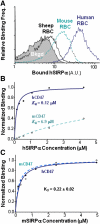
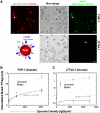
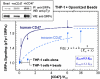
Phagocytes engulf foreign cells but not 'self' in part because self cells express CD47 as a ligand for signal regulatory protein SIRPalpha, which inhibits phagocytosis. Motivated by reports of upregulation of CD47 on both normal and cancerous stem cells [1: Jaiswal et al., 2009] and also by polymorphisms in SIRPalpha [2: Takenaka et al., 2007], we show here that inhibition of engulfment correlates with affinity of CD47 for SIRPalpha - but only at low levels of CD47. One common human polymorph of SIRPalpha is studied and binds more strongly to human-CD47 than to mouse-CD47 (K(d) approximately 0.12 microM and 6.9 microM, respectively) and does not bind sheep red blood cells (RBCs) - which are well-established targets of human macrophages; in comparison, a common mouse polymorph of SIRPalpha binds with similar affinity to human and mouse CD47 (K(d) approximately 0.22 microM). Using immunoglobulin (IgG)-opsonized particles with varying levels of either human- or mouse-CD47, the effective inhibition constants K(i) for blocking phagocytosis are then determined with both human- and mouse-derived macrophages. Only human phagocytes show significant differences in man versus mouse K(i)'s and only at CD47 levels below normal densities for RBCs. While phospho-signaling through human-SIRPalpha shows similar trends, consistent again with the affinity differences, saturating levels of CD47 (>K(i)) can signal and inhibit phagocytosis regardless of man versus mouse. Quantitative analyses here prompt more complete characterizations of both CD47 levels and SIRPalpha polymorphisms when attempting to study in vivo effects of these key proteins in innate immunity.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Takenaka K, Prasolava TK, Wang JC, Mortin-Toth SM, Khalouei S, Gan OI, Dick JE, Danska JS. Polymorphism in Sirpa modulates engraftment of human hematopoietic stem cells. Nat Immunol. 2007;8(12):1313–23. - PubMed
-
- Turrini F, Mannu F, Arese P, Yuan J, Low PS. Characterization of the autologous antibodies that opsonize erythrocytes with clustered integral membrane proteins. Blood. 1993;81(11):3146–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

