Crystal structures of human choline kinase isoforms in complex with hemicholinium-3: single amino acid near the active site influences inhibitor sensitivity
- PMID: 20299452
- PMCID: PMC2871500
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.039024
Crystal structures of human choline kinase isoforms in complex with hemicholinium-3: single amino acid near the active site influences inhibitor sensitivity
Abstract
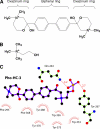
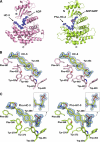
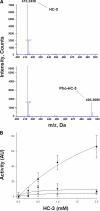
Human choline kinase (ChoK) catalyzes the first reaction in phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis and exists as ChoKalpha (alpha1 and alpha2) and ChoKbeta isoforms. Recent studies suggest that ChoK is implicated in tumorigenesis and emerging as an attractive target for anticancer chemotherapy. To extend our understanding of the molecular mechanism of ChoK inhibition, we have determined the high resolution x-ray structures of the ChoKalpha1 and ChoKbeta isoforms in complex with hemicholinium-3 (HC-3), a known inhibitor of ChoK. In both structures, HC-3 bound at the conserved hydrophobic groove on the C-terminal lobe. One of the HC-3 oxazinium rings complexed with ChoKalpha1 occupied the choline-binding pocket, providing a structural explanation for its inhibitory action. Interestingly, the HC-3 molecule co-crystallized with ChoKbeta was phosphorylated in the choline binding site. This phosphorylation, albeit occurring at a very slow rate, was confirmed experimentally by mass spectroscopy and radioactive assays. Detailed kinetic studies revealed that HC-3 is a much more potent inhibitor for ChoKalpha isoforms (alpha1 and alpha2) compared with ChoKbeta. Mutational studies based on the structures of both inhibitor-bound ChoK complexes demonstrated that Leu-401 of ChoKalpha2 (equivalent to Leu-419 of ChoKalpha1), or the corresponding residue Phe-352 of ChoKbeta, which is one of the hydrophobic residues neighboring the active site, influences the plasticity of the HC-3-binding groove, thereby playing a key role in HC-3 sensitivity and phosphorylation.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Differential role of human choline kinase alpha and beta enzymes in lipid metabolism: implications in cancer onset and treatment.PLoS One. 2009 Nov 12;4(11):e7819. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007819. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19915674 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of human choline kinase alpha and beta in carcinogenesis: a different role in lipid metabolism and biological functions.Adv Enzyme Regul. 2011;51(1):183-94. doi: 10.1016/j.advenzreg.2010.09.010. Epub 2010 Oct 28. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2011. PMID: 21035492 Review.
-
Choline kinase alpha-Putting the ChoK-hold on tumor metabolism.Prog Lipid Res. 2016 Jul;63:28-40. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Apr 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2016. PMID: 27073147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New non-symmetrical choline kinase inhibitors.Bioorg Med Chem. 2013 Nov 15;21(22):7146-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Bioorg Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24080101
-
The mechanism of allosteric coupling in choline kinase α1 revealed by the action of a rationally designed inhibitor.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013 Apr 22;52(17):4582-6. doi: 10.1002/anie.201209660. Epub 2013 Feb 25. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2013. PMID: 23441033
Cited by
-
Choline Kinase, A Novel Drug Target for the Inhibition of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Antibiotics (Basel). 2017 Sep 25;6(4):20. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics6040020. Antibiotics (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28946671 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor alph4+beta2 through a Ligand-Independent PI3Kbeta Mechanism That Is Enhanced by TNFalpha and the Jak2/p38Mapk Pathways.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 30;10(11):e0143319. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143319. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26619345 Free PMC article.
-
Bi-allelic variants in CHKA cause a neurodevelopmental disorder with epilepsy and microcephaly.Brain. 2022 Jun 30;145(6):1916-1923. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac074. Brain. 2022. PMID: 35202461 Free PMC article.
-
Plasmodium falciparum Choline Kinase Inhibition Leads to a Major Decrease in Phosphatidylethanolamine Causing Parasite Death.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 12;6:33189. doi: 10.1038/srep33189. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27616047 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Non-Congeneric Derivatives of the Choline Kinase Alpha Inhibitor ICL-CCIC-0019.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jul 14;13(7):1078. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13071078. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34371769 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Pelech S. L., Vance D. E. (1984) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 779, 217–251 - PubMed
-
- Kent C. (1990) Prog. Lipid Res. 29, 87–105 - PubMed
-
- Aoyama C., Liao H., Ishidate K. (2004) Prog. Lipid Res. 43, 266–281 - PubMed
-
- Exton J. H. (1990) J. Biol. Chem. 265, 1–4 - PubMed
-
- Aoyama C., Nakashima K., Ishidate K. (1998) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1393, 179–185 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

