The RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) directly increases the elongation rate of RNA polymerase I and is required for efficient regulation of rRNA synthesis
- PMID: 20299458
- PMCID: PMC2863250
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115220
The RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) directly increases the elongation rate of RNA polymerase I and is required for efficient regulation of rRNA synthesis
Abstract
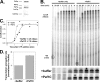
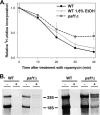
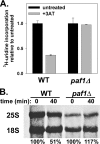
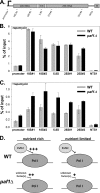
The rate of ribosome synthesis is proportional to the rate of cell proliferation; thus, transcription of rRNA by RNA polymerase I (Pol I) is an important target for the regulation of this process. Most previous investigations into mechanisms that regulate the rate of ribosome synthesis have focused on the initiation step of transcription by Pol I; however, recent studies in yeast and mammals have identified factors that influence transcription elongation by Pol I. The RNA polymerase-associated factor 1 complex (Paf1C) is a transcription elongation factor with known roles in Pol II transcription. We previously identified a role for Paf1C in transcription elongation by Pol I. In this study, genetic interactions between genes for Paf1C and Pol I subunits confirm this conclusion. In vitro studies demonstrate that purified Paf1C directly increases the rate of transcription elongation by Pol I. Finally, we show that Paf1C function is required for efficient control of Pol I transcription in response to target of rapamycin (TOR) signaling or amino acid limitation. These studies demonstrate that Paf1C plays an important direct role in cellular control of rRNA expression.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

