Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication in cultured cells and mice by a peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomer
- PMID: 20299495
- PMCID: PMC7109675
- DOI: 10.1093/jac/dkq074
Inhibition of Japanese encephalitis virus replication in cultured cells and mice by a peptide-conjugated morpholino oligomer
Abstract
Background: Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) has a significant impact on public health throughout Asia, and there is a pressing need for development of new therapeutics against it.
Methods: Peptide-conjugated phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PPMOs) are antisense agents that enter cells readily and interfere with gene expression. Four PPMOs, targeting various locations in the JEV genome, were evaluated for antiviral activity against JEV in cultured cells and the mouse model of JEV infection.
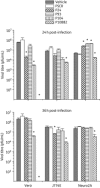
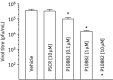
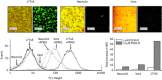
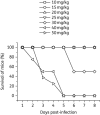
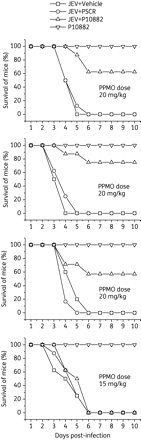
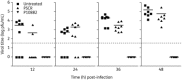
Results: A PPMO (P10882) targeting the JEV 3' cyclization sequence (3'CSI) had significant antiviral activity in Vero (epithelial), Neuro2A (neuronal) and J774E (macrophage) cells at concentrations that were not cytotoxic. P10882 added before infection suppressed JEV replication to an undetectable level in Vero cells and produced a 93% and 66% reduction in titre in J774E and Neuro2A cells, respectively, when measured at 24 h post-infection. In uninfected cells, fluorescein-labelled PPMOs entered J774E cells most efficiently, followed by Vero and Neuro2A cells. The antiviral effect of P10882 was also demonstrated in vivo, where 60%-80% of 1-week-old mice treated intracerebrally with a 20 mg/kg dose of P10882 every 12 h for 5 days were protected from a lethal dose of JEV and showed an undetectable level of virus in brain tissue at 2 days post-infection.
Conclusions: P10882, which targets sequence that is highly conserved across members of the JEV serocomplex, was previously shown to be effective in a mouse model of West Nile disease, and represents a candidate antiviral agent against members of the JEV serocomplex.
Figures
References
-
- Solomon T, Vaughn DW. Pathogenesis and clinical features of Japanese encephalitis and West Nile virus infections. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2002;267:171–94. - PubMed
-
- Summerton J, Weller D. Morpholino antisense oligomers: design, preparation, and properties. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:187–95. - PubMed
-
- Stein D, Foster E, Huang SB, et al. A specificity comparison of four antisense types: morpholino, 2′-O-methyl RNA, DNA, and phosphorothioate DNA. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev. 1997;7:151–7. - PubMed
-
- Abes S, Moulton HM, Clair P, et al. Vectorization of morpholino oligomers by the (R-Ahx-R)4 peptide allows efficient splicing correction in the absence of endosomolytic agents. J Control Release. 2006;116:304–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

