Aspergillus niger: an unusual cause of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
- PMID: 20299503
- PMCID: PMC3052473
- DOI: 10.1099/jmm.0.018309-0
Aspergillus niger: an unusual cause of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis
Abstract
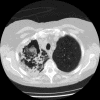
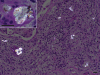
Infections due to Aspergillus species cause significant morbidity and mortality. Most are attributed to Aspergillus fumigatus, followed by Aspergillus flavus and Aspergillus terreus. Aspergillus niger is a mould that is rarely reported as a cause of pneumonia. A 72-year-old female with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and temporal arteritis being treated with steroids long term presented with haemoptysis and pleuritic chest pain. Chest radiography revealed areas of heterogeneous consolidation with cavitation in the right upper lobe of the lung. Induced bacterial sputum cultures, and acid-fast smears and cultures were negative. Fungal sputum cultures grew A. niger. The patient clinically improved on a combination therapy of empiric antibacterials and voriconazole, followed by voriconazole monotherapy. After 4 weeks of voriconazole therapy, however, repeat chest computed tomography scanning showed a significant progression of the infection and near-complete necrosis of the right upper lobe of the lung. Serum voriconazole levels were low-normal (1.0 microg ml(-1), normal range for the assay 0.5-6.0 microg ml(-1)). A. niger was again recovered from bronchoalveolar lavage specimens. A right upper lobectomy was performed, and lung tissue cultures grew A. niger. Furthermore, the lung histopathology showed acute and organizing pneumonia, fungal hyphae and oxalate crystallosis, confirming the diagnosis of invasive A. niger infection. A. niger, unlike A. fumigatus and A. flavus, is less commonly considered a cause of invasive aspergillosis (IA). The finding of calcium oxalate crystals in histopathology specimens is classic for A. niger infection and can be helpful in making a diagnosis even in the absence of conidia. Therapeutic drug monitoring may be useful in optimizing the treatment of IA given the wide variations in the oral bioavailability of voriconazole.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of the combination of voriconazole and caspofungin in experimental pulmonary aspergillosis by different Aspergillus species.Mycopathologia. 2014 Feb;177(1-2):11-8. doi: 10.1007/s11046-013-9719-z. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Mycopathologia. 2014. PMID: 24306184 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive pulmonary aspergillosis due to Aspergillus terreus: value of DNA, galactomannan and (1->3)-beta-D-glucan detection in serum samples as an adjunct to diagnosis.J Med Microbiol. 2010 Dec;59(Pt 12):1519-1523. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.023630-0. Epub 2010 Aug 19. J Med Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20724511
-
Quinupristin/dalfopristin and voriconazole controlled Staphylococcus epidermidis pneumonia and chronic necrotizing aspergillosis in a patient with severe lung degradation consequent to multiple treatments for Hodgkin's lymphoma.J Infect Chemother. 2006 Dec;12(6):391-5. doi: 10.1007/s10156-006-0495-2. Epub 2007 Jan 18. J Infect Chemother. 2006. PMID: 17235646
-
Management of invasive aspergillosis in patients with COPD: rational use of voriconazole.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2009;4:279-87. doi: 10.2147/copd.s4229. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2009. PMID: 19684861 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Voriconazole as an effective therapy against pulmonary aspergillosis in a man with immunodeficiency virus-infection: a case report].Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2007 Mar;81(2):200-5. doi: 10.11150/kansenshogakuzasshi1970.81.200. Kansenshogaku Zasshi. 2007. PMID: 17447480 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Aspergillus niger upregulated glycerolipid metabolism and ethanol utilization pathway under ethanol stress.Microbiologyopen. 2020 Jan;9(1):e00948. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.948. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Microbiologyopen. 2020. PMID: 31646764 Free PMC article.
-
Histopathological implications of Aspergillus infection in lung.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:809798. doi: 10.1155/2013/809798. Epub 2013 Nov 20. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 24347836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Insights into the Cyp51 Contribution to Azole Resistance in Aspergillus Section Nigri.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Jun 24;63(7):e00543-19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00543-19. Print 2019 Jul. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019. PMID: 31061160 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the combination of voriconazole and caspofungin in experimental pulmonary aspergillosis by different Aspergillus species.Mycopathologia. 2014 Feb;177(1-2):11-8. doi: 10.1007/s11046-013-9719-z. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Mycopathologia. 2014. PMID: 24306184 Free PMC article.
-
Food Hygiene Practices at the Ghana School Feeding Programme in Wa and Cape Coast Cities.J Environ Public Health. 2020 May 12;2020:9083716. doi: 10.1155/2020/9083716. eCollection 2020. J Environ Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32454843 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Araiza, J., Canseco, P. & Bonifaz, A. (2006). Otomycosis: clinical and mycological study of 97 cases. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 127, 251–254. - PubMed
-
- Baddley, J. W., Marr, K. A., Andes, D. R., Walsh, T. J., Kauffman, C. A., Kontoyiannis, D. P., Ito, J. I., Balajee, S. A., Pappas, P. G. & Moser, S. A. (2009). Patterns of susceptibility of Aspergillus isolates recovered from patients enrolled in the Transplant-Associated Infection Surveillance Network. J Clin Microbiol 47, 3271–3275. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baron, O., Guillaumé, B., Moreau, P., Germaud, P., Despins, P., De Lajartre, A. Y. & Michaud, J. L. (1998). Aggressive surgical management in localized pulmonary mycotic and nonmycotic infections for neutropenic patients with acute leukemia: report of eighteen cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 115, 63–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

