Adiposity-independent sympathetic activity in black men
- PMID: 20299621
- PMCID: PMC2886690
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00058.2010
Adiposity-independent sympathetic activity in black men
Abstract
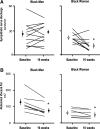
Obesity is thought to lead to sympathetic overactivity as a compensatory adjustment to weight gain. However, most of the experimental support for the hypothesis has been derived from white cohorts. Our previous study in blacks indicated that sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) is closely correlated with body mass index only in women, whereas, in black men, SNA is elevated and dissociated from adiposity (Abate et al., Hypertension 38: 379-383, 2001). To further determine whether total and regional adiposity are determinants of SNA in blacks, we performed a prospective weight loss study in 12 normotensive obese black men and 9 obese black women. SNA, body mass index, and abdominal fat mass were measured before and 16 wk after hypocaloric diet. The major new findings are that, in obese black men, the dietary-induced weight loss of 11.3+/-0.8 kg resulted in reduction in plasma leptin, insulin, and visceral abdominal fat but had no effect on SNA (from baseline of 26+/-4 to 28+/-3 bursts/min, P=not significant). In contrast, in black women, weight loss of 8.0+/-0.9 kg caused similar reductions in plasma leptin, insulin, and visceral abdominal fat and led to a reduction in SNA by 40% (from baseline of 22+/-2 to 13+/-3 bursts/min, P<0.05). In conclusion, these new data from this prospective study provide strong support for a major adiposity-independent sympathetic activity in black men and adiposity-related sympathetic activity in black women.
Figures

References
-
- Abate NI, Mansour YH, Tuncel M, Arbique D, Chavoshan B, Kizilbash A, Howell-Stampley T, Vongpatanasin W, Victor RG. Overweight and sympathetic overactivity in Black Americans. Hypertension 38: 379–383, 2001 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez GE, Ballard TP, Beske SD, Davy KP. Subcutaneous obesity is not associated with sympathetic neural activation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 287: H414–H418, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Alvarez GE, Beske SD, Ballard TP, Davy KP. Sympathetic neural activation in visceral obesity. Circulation 106: 2533–2536, 2002 - PubMed
-
- American Heart Association Heart and Stroke Statistics—2009 Update. Dallas, TX: American Heart Association, 2009
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

