Signaling to NF-kappaB: regulation by ubiquitination
- PMID: 20300215
- PMCID: PMC2829959
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a003350
Signaling to NF-kappaB: regulation by ubiquitination
Abstract
The NF-kappaB pathway is a ubiquitous stress response that activates the NF-kappaB family of transcription factors. Antigen receptors, receptors of the innate immune system, and certain intracellular stressors are potent activators of this pathway. The transcriptional program that is activated is both antiapoptotic and highly proinflammatory. Indeed, any compromise in engagement of the pathway results in immunodeficiency, whereas constitutive activation generates a sustained inflammatory response that may promote malignancy. As such, NF-kappaB activation is under tight regulation by a number of post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation and ubiquitination. This article attempts to synthesize our current knowledge regarding the regulation of NF-kappaB signaling by ubiquitination, specifically highlighting the biochemical basis for both positive and negative feedback loops that function in unison to generate coordinated signals that are essential for the viability of metazoan animals.
Figures
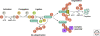
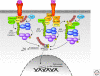
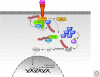
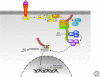

References
-
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R 2004. Toll signaling: RIPping off the TNF pathway. Nat Immunol 5:472–474 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand MJ, Doiron K, Labbe K, Korneluk RG, Barker PA, Saleh M 2009. Cellular inhibitors of apoptosis cIAP1 and cIAP2 are required for innate immunity signaling by the pattern recognition receptors NOD1 and NOD2. Immunity 30:789–801 - PubMed
-
- Bertrand MJ, Milutinovic S, Dickson KM, Ho WC, Boudreault A, Durkin J, Gillard JW, Jaquith JB, Morris SJ, Barker PA 2008. cIAP1 and cIAP2 facilitate cancer cell survival by functioning as E3 ligases that promote RIP1 ubiquitination. Mol Cell 30:689–700 - PubMed
-
- Bhoj VG, Chen ZJ 2009. Ubiquitylation in innate and adaptive immunity. Nature 458:430–437 - PubMed
-
- Boone DL, Turer EE, Lee EG, Ahmad RC, Wheeler MT, Tsui C, Hurley P, Chien M, Chai S, Hitotsumatsu O, et al.2004. The ubiquitin-modifying enzyme A20 is required for termination of Toll-like receptor responses. Nat Immunol 5:1052–1060 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
