The dual role of calcium as messenger and stressor in cell damage, death, and survival
- PMID: 20300548
- PMCID: PMC2838366
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/546163
The dual role of calcium as messenger and stressor in cell damage, death, and survival
Abstract
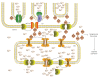
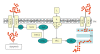
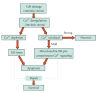
Ca(2+) is an important second messenger participating in many cellular activities; when physicochemical insults deregulate its delicate homeostasis, it acts as an intrinsic stressor, producing/increasing cell damage. Damage elicits both repair and death responses; intriguingly, in those responses Ca(2+) also participates as second messenger. This delineates a dual role for Ca(2+) in cell stress, making difficult to separate the different and multiple mechanisms required for Ca(2+)-mediated control of cell survival and apoptosis. Here we attempt to disentangle the two scenarios, examining on the one side, the events implicated in deregulated Ca(2+) toxicity and the mechanisms through which this elicits reparative or death pathways; on the other, reviewing the role of Ca(2+) as a messenger in the transduction of these same signaling events.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: interactions between cell death and survival pathways.Arch Toxicol. 2013 Oct;87(10):1743-86. doi: 10.1007/s00204-013-1110-9. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Arch Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23982889 Review.
-
Calcium signaling and cell cycle: Progression or death.Cell Calcium. 2018 Mar;70:3-15. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2017.07.006. Epub 2017 Jul 25. Cell Calcium. 2018. PMID: 28801101 Review.
-
Various Aspects of Calcium Signaling in the Regulation of Apoptosis, Autophagy, Cell Proliferation, and Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 6;21(21):8323. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218323. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33171939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor-isoform diversity in cell death and survival.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Oct;1843(10):2164-83. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2014.03.007. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24642269 Review.
-
Disrupted calcium homeostasis is involved in elevated zinc ion-induced photoreceptor cell death.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014 Oct 15;560:44-51. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2014.07.014. Epub 2014 Jul 19. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2014. PMID: 25051343
Cited by
-
A Review on Differences in Effects on Normal and Malignant Cells and Tissues to Electroporation-Based Therapies: A Focus on Calcium Electroporation.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018 Jan 1;17:1533033818788077. doi: 10.1177/1533033818788077. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 30012047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus Perturbs the Host Cell Ca2+ Homeostasis To Promote Cell Death.mBio. 2020 Dec 15;11(6):e02250-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02250-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 33323513 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant-Chemosynthetic Biosensors for Probing Cell Surface Signaling of Red Blood Cells and Other Cells.Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025 Jan 3;3(2):95-110. doi: 10.1021/cbmi.4c00067. eCollection 2025 Feb 24. Chem Biomed Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40018647 Free PMC article.
-
Candidalysin triggers epithelial cellular stresses that induce necrotic death.Cell Microbiol. 2021 Oct;23(10):e13371. doi: 10.1111/cmi.13371. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Cell Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34085369 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of long-term dehydration on stress markers, blood parameters, and tissue morphology in the dromedary camel (Camelus dromedarius).Front Vet Sci. 2023 Dec 5;10:1236425. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1236425. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 38116506 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1985;260(6):3440–3450. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology. 2003;4(7):517–529. - PubMed
-
- Lee HC. Cyclic ADP-ribose: a calcium mobilizing metabolite of NAD+ . Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 1994;138(1-2):229–235. - PubMed
-
- Putney JW, Jr., Broad LM, Braun F-J, Lievremont J-P, Bird GStJ. Mechanisms of capacitative calcium entry. Journal of Cell Science. 2001;114(12):2223–2229. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

