Decreasing the homodimer interaction: a common mechanism shared by the deltaG91 mutation and deamidation in betaA3-crystallin
- PMID: 20300566
- PMCID: PMC2838740
Decreasing the homodimer interaction: a common mechanism shared by the deltaG91 mutation and deamidation in betaA3-crystallin
Abstract
Purpose: Cataracts can be broadly divided into two types: congenital cataracts and age-related cataracts. DeltaG91 is a previously discovered congenital mutation in betaA3-crystallin that impairs protein solubility. On the other hand, the deamidation of beta-crystallin is a significant feature in aged and cataractous lenses. Several deamidation sites were also identified in betaA3-crystallin. The present study is to compare the functional consequence of DeltaG91 mutation and the deamidation of betaA3-crystallin in terms of folding properties and protein-protein interaction.
Methods: Protein secondary structure and hydrophobic properties were investigated by in silica analysis of the wild type and mutants sequences. Full-length betaA3-crystallin was cloned into a mammalian two-hybrid system in order to investigate protein-protein interactions. Deletion and deamidation were introduced by site-directed mutagenesis protocols. Both the Q85 and Q180 deamidation sites were substituted with glutamic acid residues to mimic deamidation. Different combinations of plasmid constructs were transfected in HeLa cells, and changes of protein-protein interactions were analyzed by the luciferase assay.
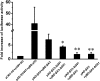
Results: Bioinformatics prediction suggested that DeltaG91 mutation alters both the predicted secondary structure and hydrophobic character of betaA3-crystallin, while deamidation only exhibits minimal effects. Mammalian two-hybrid results indicated that both DeltaG91 mutation and Q85/Q180 deamidation could significantly decrease the interaction of the betaA3-crystallin homodimer.
Conclusion: Our results provided evidence that both mutations involved in congenital cataracts and deamidation in aged lenses commonly altered protein-protein interaction between human lens betaA3-crystallins, which may lead to protein insolubilization and contribute to cataracts.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Deamidation alters interactions of beta-crystallins in hetero-oligomers.Mol Vis. 2009;15:241-9. Epub 2009 Jan 28. Mol Vis. 2009. PMID: 19190732 Free PMC article.
-
Deamidation alters the structure and decreases the stability of human lens betaA3-crystallin.Biochemistry. 2007 Jul 31;46(30):8861-71. doi: 10.1021/bi700487q. Epub 2007 Jul 7. Biochemistry. 2007. PMID: 17616172 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction of βA3-Crystallin with Deamidated Mutants of αA- and αB-Crystallins.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 11;10(12):e0144621. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0144621. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26657544 Free PMC article.
-
βA3/A1-crystallin: more than a lens protein.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015 Jan;44:62-85. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 13. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25461968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
βA3/A1-crystallin and persistent fetal vasculature (PFV) disease of the eye.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1860(1 Pt B):287-98. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.05.017. Epub 2015 May 31. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26022148 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted Exome Sequencing of Congenital Cataracts Related Genes: Broadening the Mutation Spectrum and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations in 27 Chinese Han Families.Sci Rep. 2017 Apr 27;7(1):1219. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01182-9. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28450710 Free PMC article.
-
Cataract-causing mutation S228P promotes βB1-crystallin aggregation and degradation by separating two interacting loops in C-terminal domain.Protein Cell. 2016 Jul;7(7):501-15. doi: 10.1007/s13238-016-0284-3. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Protein Cell. 2016. PMID: 27318838 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation screening and genotype phenotype correlation of α-crystallin, γ-crystallin and GJA8 gene in congenital cataract.Mol Vis. 2011 Mar 11;17:693-707. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21423869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reddy MA, Bateman OA, Chakarova C, Ferris J, Berry V, Lomas E, Sarra R, Smith MA, Moore AT, Bhattacharya SS, Slingsby C. Characterization of the G91del CRYBA1/3-crystallin protein: a cause of human inherited cataract. Hum Mol Genet. 2004;13:945–53. - PubMed
-
- Slingsby C, Bateman OA. Quaternary interactions in eye lens beta-crystallins: basic and acidic subunits of beta-crystallins favor heterologous association. Biochemistry. 1990;29:6592–9. - PubMed
-
- Ajaz MS, Ma Z, Smith DL, Smith JB. Size of human lens beta-crystallin aggregates are distinguished by N-terminal truncation of betaB1. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:11250–5. - PubMed
-
- Lu S, Zhao C, Jiao H, Kere J, Tang X, Zhao F, Zhang X, Zhao K, Larsson C. Two Chinese families with pulverulent congenital cataracts and deltaG91 CRYBA1 mutations. Mol Vis. 2007;13:1154–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
