Size functions for the morphological analysis of melanocytic lesions
- PMID: 20300598
- PMCID: PMC2838225
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/621357
Size functions for the morphological analysis of melanocytic lesions
Abstract
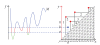
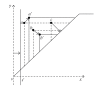
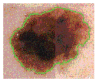
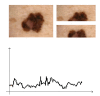
Size Functions and Support Vector Machines are used to implement a new automatic classifier of melanocytic lesions. This is mainly based on a qualitative assessment of asymmetry, performed by halving images by several lines through the center of mass, and comparing the two halves in terms of color, mass distribution, and boundary. The program is used, at clinical level, with two thresholds, so that comparison of the two outputs produces a report of low-middle-high risk. Experimental results on 977 images, with cross-validation, are reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automatic differentiation of melanoma from melanocytic nevi with multispectral digital dermoscopy: a feasibility study.J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001 Feb;44(2):207-18. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.110395. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001. PMID: 11174377
-
Computer-aided diagnosis of skin lesions using conventional digital photography: a reliability and feasibility study.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 4;8(11):e76212. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0076212. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24223698 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Comparison of Color Asymmetry Features for Automatic Melanoma Detection.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021 Nov;2021:3753-3756. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9631103. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021. PMID: 34892052
-
Role of In Vivo Reflectance Confocal Microscopy in the Analysis of Melanocytic Lesions.Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018 Apr;26(1):64-67. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat. 2018. PMID: 29782304 Review.
-
Improved discrimination of melanotic schwannoma from melanocytic lesions by combined morphological and GNAQ mutational analysis.Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Dec;120(6):755-64. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0749-z. Epub 2010 Sep 24. Acta Neuropathol. 2010. PMID: 20865267 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of skin barrier function using skin images with topological data analysis.NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2020 Dec 18;6(1):40. doi: 10.1038/s41540-020-00160-8. NPJ Syst Biol Appl. 2020. PMID: 33339832 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Melanoma: A Meta-analysis.JAMA Dermatol. 2019 Nov 1;155(11):1291-1299. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1375. JAMA Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 31215969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kopf AW, Salopek TG, Slade J, Marghoob AA, Bart RS. Techniques of cutaneous examination for the detection of skin cancer. Cancer. 1994;75(2):684–690. - PubMed
-
- Stanganelli I, Clemente C, Mihm MC., Jr. CD Melanoma cutaneo—Atlante multimediale interattivo per la prevenzione, la diagnosi e la terapia del Melanoma e delle lesioni pigmentate cutanee. Istituto Oncologico Romagnolo Ed., MAF Torino, Italy, 2001.
-
- Hintz-Madsen M, Kai Hansen L, Larsen J, Olesen E, Drzewiecki KT. Detection of malignant melanoma using neural classifiers. Solving Engineering Problems with Neural Networks, Proceedings of the International Conference Engineerings Applications of Neural Networks (EANN ’96) 1996;96:395–398.
-
- Seidenari S, Pellacani G, Giannetti A. Digital videomicroscopy and image analysis with automatic classification for detection of thin melanomas. Melanoma Research. 1999;9(2):163–171. - PubMed
-
- Rosado B, Menzies S, Harbauer A, et al. Accuracy of computer diagnosis of melanoma: a quantitative meta-analysis. Archives of Dermatology. 2003;139(3):361–367. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources