Fatal cardiac arrhythmia and long-QT syndrome in a new form of congenital generalized lipodystrophy with muscle rippling (CGL4) due to PTRF-CAVIN mutations
- PMID: 20300641
- PMCID: PMC2837386
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000874
Fatal cardiac arrhythmia and long-QT syndrome in a new form of congenital generalized lipodystrophy with muscle rippling (CGL4) due to PTRF-CAVIN mutations
Abstract
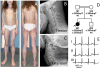
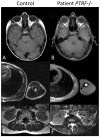
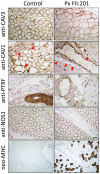
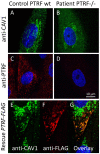
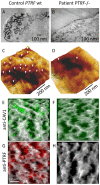
We investigated eight families with a novel subtype of congenital generalized lipodystrophy (CGL4) of whom five members had died from sudden cardiac death during their teenage years. ECG studies revealed features of long-QT syndrome, bradycardia, as well as supraventricular and ventricular tachycardias. Further symptoms comprised myopathy with muscle rippling, skeletal as well as smooth-muscle hypertrophy, leading to impaired gastrointestinal motility and hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in some children. Additionally, we found impaired bone formation with osteopenia, osteoporosis, and atlanto-axial instability. Homozygosity mapping located the gene within 2 Mbp on chromosome 17. Prioritization of 74 candidate genes with GeneDistiller for high expression in muscle and adipocytes suggested PTRF-CAVIN (Polymerase I and transcript release factor/Cavin) as the most probable candidate leading to the detection of homozygous mutations (c.160delG, c.362dupT). PTRF-CAVIN is essential for caveolae biogenesis. These cholesterol-rich plasmalemmal vesicles are involved in signal-transduction and vesicular trafficking and reside primarily on adipocytes, myocytes, and osteoblasts. Absence of PTRF-CAVIN did not influence abundance of its binding partner caveolin-1 and caveolin-3. In patient fibroblasts, however, caveolin-1 failed to localize toward the cell surface and electron microscopy revealed reduction of caveolae to less than 3%. Transfection of full-length PTRF-CAVIN reestablished the presence of caveolae. The loss of caveolae was confirmed by Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM) in combination with fluorescent imaging. PTRF-CAVIN deficiency thus presents the phenotypic spectrum caused by a quintessential lack of functional caveolae.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Garg A. Acquired and inherited lipodystrophies. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1220–1234. - PubMed
-
- Magre J, Delepine M, Khallouf E, Gedde-Dahl T, Jr, Van Maldergem L, et al. Identification of the gene altered in Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy on chromosome 11q13. Nat Genet. 2001;28:365–370. - PubMed
-
- Agarwal AK, Arioglu E, De Almeida S, Akkoc N, Taylor SI, et al. AGPAT2 is mutated in congenital generalized lipodystrophy linked to chromosome 9q34. Nat Genet. 2002;31:21–23. - PubMed
-
- Kim CA, Delepine M, Boutet E, El Mourabit H, Le Lay S, et al. Association of a homozygous nonsense caveolin-1 mutation with Berardinelli-Seip congenital lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1129–1134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

