Laparoscopic exploration in pediatric surgery emergencies
- PMID: 20302204
- PMCID: PMC3019036
Laparoscopic exploration in pediatric surgery emergencies
Abstract
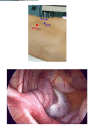
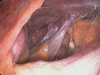
The laparoscopic approach of pediatric surgery emergencies represents a specific preoccupation in hospitals everywhere in the world. Nowadays, when confronted with this pathology, pediatric surgeons are able to apply certain well-defined therapeutic protocols, depending on the technical equipment at their disposal and their laparoscopic expertise and training. We hereby present some of the surgical pediatric emergencies that have been subjected to minimally invasive celioscopic techniques, in the Department of Pediatric Surgery "Maria Sklodowska Curie" Hospital, from August 1999 to July 2007. Out of 83 exploratory laparoscopies, 12 were performed for emergency pathology, other than acute appendicitis (in its various forms, including peritonitis) or acute cholecystitis. However, during the above-mentioned period, the number of therapeutic laparoscopies for emergencies has grown significantly (239 from a total of 663 laparoscopies), reflecting to a large extent the activity of a clinic with an emergency surgery profile. The authors conclude that exploratory laparoscopies in pediatric surgery emergencies are suited for surgical teams with a solid experience in celioscopy and a certain professional maturity, necessary to correctly appreciate the surgical and anesthetic risks involved by each individual case. It is not recommended that inexperienced laparoscopic surgeons embark on the "adventure" of this minimally invasive approach for this type of pathology. Only when the training and learning process is fully and correctly completed, specialists are offered the advantage of continuing a celioscopic exploration by performing a minimally invasive therapeutic procedure, even for a pediatric emergency case.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Exploratory laparoscopy--diagnosis method in pediatric surgery pathology.J Med Life. 2009 Jul-Sep;2(3):288-95. J Med Life. 2009. PMID: 20112473 Free PMC article.
-
[Training for pediatric surgeons through the keyhole].Orv Hetil. 2018 Oct;159(43):1747-1753. doi: 10.1556/650.2018.31189. Orv Hetil. 2018. PMID: 30346239 Hungarian.
-
Minimally invasive surgery: the pediatric surgery experience.J Am Coll Surg. 1998 May;186(5):542-4. doi: 10.1016/s1072-7515(98)00087-8. J Am Coll Surg. 1998. PMID: 9583694
-
Advances in minimally invasive surgery in pediatrics.Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2010 Jun;12(3):211-4. doi: 10.1007/s11894-010-0109-0. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2010. PMID: 20425470 Review.
-
[Laparoscopic training--the guarantee of a future in pediatric surgery].Chirurgia (Bucur). 2009 May-Jun;104(3):255-8. Chirurgia (Bucur). 2009. PMID: 19601455 Review. Romanian.
Cited by
-
The role of laparoscopy in suspicious abdomen pain in children.Pak J Med Sci. 2013 Jul;29(4):1042-5. Pak J Med Sci. 2013. PMID: 24353684 Free PMC article.
-
Laparoscopic surgery complications: postoperative peritonitis.J Med Life. 2012 Sep 15;5(3):288-96. Epub 2012 Sep 25. J Med Life. 2012. PMID: 23049630 Free PMC article.
-
The electromagnetic bio-field: clinical experiments and interferences.J Med Life. 2012 Jun 12;5(2):139-44. Epub 2012 Jun 18. J Med Life. 2012. PMID: 22802878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berci G. Complication of laparoscopic Surgery . Surgical Endoscopy. 1998;8:689–691. - PubMed
-
- Reinberg Y, Gonzalez R. Laparoscopic urological surgery in children . Semin Urol. 1992;10:161–163. - PubMed
-
- De Mingo Misena L. Laparoscopic in pediatric surgery. Cir Pediatr. 1993;6:178–181. - PubMed
-
- Lobe ET. Laparoscopic surgery in children. Curr Probl Surg. 1998;35:869–948. - PubMed
-
- Humphrey GME, Najmaldin A. Laparoscopic appendicectomy in chilhood. Pediatr Surg Int. 1995;10:86–89.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
