B-lymphocyte stimulator/a proliferation-inducing ligand heterotrimers are elevated in the sera of patients with autoimmune disease and are neutralized by atacicept and B-cell maturation antigen-immunoglobulin
- PMID: 20302641
- PMCID: PMC2888197
- DOI: 10.1186/ar2959
B-lymphocyte stimulator/a proliferation-inducing ligand heterotrimers are elevated in the sera of patients with autoimmune disease and are neutralized by atacicept and B-cell maturation antigen-immunoglobulin
Abstract
Introduction: B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS) and a proliferation-inducing ligand (APRIL) are members of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family that regulate B-cell maturation, survival, and function. They are overexpressed in a variety of autoimmune diseases and reportedly exist in vivo not only as homotrimers, but also as BLyS/APRIL heterotrimers.
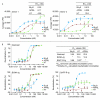
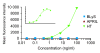
Methods: A proprietary N-terminal trimerization domain was used to produce recombinant BLyS/APRIL heterotrimers. Heterotrimer biologic activity was compared with that of BLyS and APRIL in a 4-hour signaling assay by using transmembrane activator and CAML interactor (TACI)-transfected Jurkat cells and in a 4-day primary human B-cell proliferation assay. A bead-based immunoassay was developed to quantify native heterotrimers in human sera from healthy donors (n = 89) and patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE; n = 89) or rheumatoid arthritis (RA; n = 30). Heterotrimer levels were compared with BLyS and APRIL homotrimer levels in a subset of these samples.
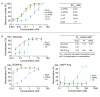
Results: The recombinant heterotrimers consisted mostly of one BLyS and two APRIL molecules. Heterotrimer signaling did not show any significant difference compared with APRIL in the TACI-Jurkat assay. Heterotrimers were less-potent inducers of B-cell proliferation than were homotrimeric BLyS or APRIL (EC(50), nMol/L: BLyS, 0.02; APRIL, 0.17; heterotrimers, 4.06). The soluble receptor fusion proteins atacicept and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-immunoglobulin (Ig) neutralized the activity of BLyS, APRIL, and heterotrimers in both cellular assays, whereas B-cell activating factor belonging to the TNF family receptor (BAFF-R)-Ig neutralized only the activity of BLyS. In human sera, significantly more patients with SLE had detectable BLyS (67% versus 18%; P < 0.0001), APRIL (38% versus 3%; P < 0.0002), and heterotrimer (27% versus 8%; P = 0.0013) levels compared with healthy donors. Significantly more patients with RA had detectable APRIL, but not BLyS or heterotrimer, levels compared with healthy donors (83% versus 3%; P < 0.0001). Heterotrimer levels weakly correlated with BLyS, but not APRIL, levels.
Conclusions: Recombinant BLyS/APRIL heterotrimers have biologic activity and are inhibited by atacicept and BCMA-Ig, but not by BAFF-R-Ig. A novel immunoassay demonstrated that native BLyS/APRIL heterotrimers, as well as BLyS and APRIL homotrimers, are elevated in patients with autoimmune diseases.
Figures

Comment in
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus and its ABCs (APRIL/BLyS complexes).Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(2):111. doi: 10.1186/ar2976. Epub 2010 Apr 22. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010. PMID: 20441604 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bossen C, Cachero TG, Tardivel A, Ingold K, Willen L, Dobles M, Scott ML, Maquelin A, Belnoue E, Siegrist CA, Chevrier S, Acha-Orbea H, Leung H, Mackay F, Tschopp J, Schneider P. TACI, unlike BAFF-R, is solely activated by oligomeric BAFF and APRIL to support survival of activated B cells and plasmablasts. Blood. 2008;111:1004–1012. doi: 10.1182/blood-2007-09-110874. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

