Identification and evaluation of new reference genes in Gossypium hirsutum for accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data
- PMID: 20302670
- PMCID: PMC2923523
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-10-49
Identification and evaluation of new reference genes in Gossypium hirsutum for accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data
Abstract
Background: Normalizing through reference genes, or housekeeping genes, can make more accurate and reliable results from reverse transcription real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR). Recent studies have shown that no single housekeeping gene is universal for all experiments. Thus, suitable reference genes should be the first step of any qPCR analysis. Only a few studies on the identification of housekeeping gene have been carried on plants. Therefore qPCR studies on important crops such as cotton has been hampered by the lack of suitable reference genes.
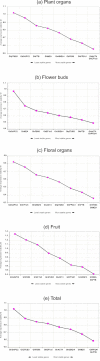
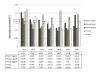
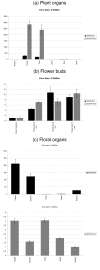
Results: By the use of two distinct algorithms, implemented by geNorm and NormFinder, we have assessed the gene expression of nine candidate reference genes in cotton: GhACT4, GhEF1alpha5, GhFBX6, GhPP2A1, GhMZA, GhPTB, GhGAPC2, GhbetaTUB3 and GhUBQ14. The candidate reference genes were evaluated in 23 experimental samples consisting of six distinct plant organs, eight stages of flower development, four stages of fruit development and in flower verticils. The expression of GhPP2A1 and GhUBQ14 genes were the most stable across all samples and also when distinct plants organs are examined. GhACT4 and GhUBQ14 present more stable expression during flower development, GhACT4 and GhFBX6 in the floral verticils and GhMZA and GhPTB during fruit development. Our analysis provided the most suitable combination of reference genes for each experimental set tested as internal control for reliable qPCR data normalization. In addition, to illustrate the use of cotton reference genes we checked the expression of two cotton MADS-box genes in distinct plant and floral organs and also during flower development.
Conclusion: We have tested the expression stabilities of nine candidate genes in a set of 23 tissue samples from cotton plants divided into five different experimental sets. As a result of this evaluation, we recommend the use of GhUBQ14 and GhPP2A1 housekeeping genes as superior references for normalization of gene expression measures in different cotton plant organs; GhACT4 and GhUBQ14 for flower development, GhACT4 and GhFBX6 for the floral organs and GhMZA and GhPTB for fruit development. We also provide the primer sequences whose performance in qPCR experiments is demonstrated. These genes will enable more accurate and reliable normalization of qPCR results for gene expression studies in this important crop, the major source of natural fiber and also an important source of edible oil. The use of bona fide reference genes allowed a detailed and accurate characterization of the temporal and spatial expression pattern of two MADS-box genes in cotton.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

