Regulation of EGFR and Notch signaling by distinct isoforms of D-cbl during Drosophila development
- PMID: 20302857
- PMCID: PMC2866751
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.03.005
Regulation of EGFR and Notch signaling by distinct isoforms of D-cbl during Drosophila development
Abstract
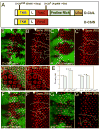
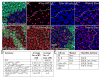
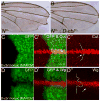
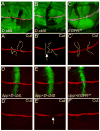
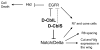
Cells receive and interpret extracellular signals to regulate cellular responses such as proliferation, cell survival and differentiation. However, proper inactivation of these signals is critical for appropriate homeostasis. Cbl proteins are E3-ubiquitin ligases that restrict receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) signaling, most notably EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor), via the endocytic pathway. Consistently, many mutant phenotypes of Drosophila cbl (D-cbl) are due to inappropriate activation of EGFR signaling. However, not all D-cbl phenotypes can be explained by increased EGFR activity. Here, we report that D-Cbl also negatively regulates Notch activity during eye and wing development. D-cbl produces two isoforms by alternative splicing. The long isoform, D-CblL, regulates the EGFR. We found that the short isoform, D-CblS, preferentially restricts Notch signaling. Specifically, our data imply that D-CblS controls the activity of the Notch ligand Delta. Taken together, these data suggest that D-Cbl controls the EGFR and Notch/Delta signaling pathways through production of two alternatively spliced isoforms during development in Drosophila.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
D-Cbl binding to Drk leads to dose-dependent down-regulation of EGFR signaling and increases receptor-ligand endocytosis.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 14;6(2):e17097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017097. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21340027 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects of Cbl isoforms on Egfr signaling in Drosophila.Mech Dev. 2006 Jun;123(6):450-62. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2006.04.001. Epub 2006 Jul 17. Mech Dev. 2006. PMID: 16844358
-
Drosophila cbl is essential for control of cell death and cell differentiation during eye development.PLoS One. 2008 Jan 16;3(1):e1447. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0001447. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18197257 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal Cbl controls biosynthesis of insulin-like peptides in Drosophila melanogaster.Mol Cell Biol. 2012 Sep;32(18):3610-23. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00592-12. Epub 2012 Jul 9. Mol Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 22778134 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of notch signaling via O-glucosylation insights from Drosophila studies.Methods Enzymol. 2010;480:375-98. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(10)80017-5. Methods Enzymol. 2010. PMID: 20816218 Review.
Cited by
-
Endocytosis at the Crossroad of Polarity and Signaling Regulation: Learning from Drosophila melanogaster and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 23;23(9):4684. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094684. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35563080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-cell autonomous control of apoptosis by ligand-independent Hedgehog signaling in Drosophila.Cell Death Differ. 2013 Feb;20(2):302-11. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2012.126. Epub 2012 Sep 28. Cell Death Differ. 2013. PMID: 23018595 Free PMC article.
-
Balanced ubiquitination determines cellular responsiveness to extracellular stimuli.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Dec;69(23):4007-16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1084-4. Epub 2012 Jul 24. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22825661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of CTP Synthase Filament Formation During DNA Endoreplication in Drosophila.Genetics. 2015 Dec;201(4):1511-23. doi: 10.1534/genetics.115.180737. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Genetics. 2015. PMID: 26482795 Free PMC article.
-
Ubiquitinations in the notch signaling pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Mar 19;14(3):6359-81. doi: 10.3390/ijms14036359. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23519106 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baker NE, Zitron AE. Drosophila eye development: Notch and Delta amplify a neurogenic pattern conferred on the morphogenetic furrow by scabrous. Mech Dev. 1995;49:173–189. - PubMed
-
- Baonza A, Casci T, Freeman M. A primary role for the epidermal growth factor receptor in ommatidial spacing in the Drosophila eye. Curr Biol. 2001;11:396–404. - PubMed
-
- Bergmann A, Agapite J, McCall K, Steller H. The Drosophila gene hid is a direct molecular target of Ras-dependent survival signaling. Cell. 1998;95:331–341. - PubMed
-
- Cagan RL, Ready DF. The emergence of order in the Drosophila pupal retina. Dev Biol. 1989;136:346–362. - PubMed
-
- Casci T, Vinos J, Freeman M. Sprouty, an intracellular inhibitor of Ras signaling. Cell. 1999;96:655–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

