Acidic calcium stores open for business: expanding the potential for intracellular Ca2+ signaling
- PMID: 20303271
- PMCID: PMC2862797
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcb.2010.02.003
Acidic calcium stores open for business: expanding the potential for intracellular Ca2+ signaling
Erratum in
- Trends Cell Biol. 2010 Nov;20(11):627
Abstract
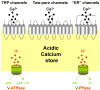
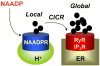
Changes in cytosolic calcium concentration are crucial for a variety of cellular processes in all cells. It has long been appreciated that calcium is stored and released from intracellular calcium stores such as the endoplasmic reticulum. However, emerging evidence indicates that calcium is also dynamically regulated by a seemingly disparate collection of acidic organelles. In this paper, we review the defining features of these 'acidic calcium stores' and highlight recent progress in understanding the mechanisms of uptake and release of calcium from these stores. We also examine the nature of calcium buffering within the stores, and summarize the physiological and pathophysiological significance of these ubiquitous organelles in calcium signaling.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000;1:11–21. - PubMed
-
- Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P. Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:552–565. - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE. Calcium signaling. Cell. 2007;131:1047–1058. - PubMed
-
- Berridge MJ. The endoplasmic reticulum: a multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium. 2002;32:235–249. - PubMed
-
- Pozzan T, Rizzuto R, Volpe P, Meldolesi J. Molecular and cellular physiology of intracellular calcium stores. Physiol Rev. 1994;74:595–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

