A novel role for the dioxin receptor in fatty acid metabolism and hepatic steatosis
- PMID: 20303349
- PMCID: PMC2910786
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.03.033
A novel role for the dioxin receptor in fatty acid metabolism and hepatic steatosis
Abstract
Background & aims: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) also known as the dioxin receptor or xenobiotic receptor is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix/period AhR nuclear translocator single minded family. The goal of this study was to determine the endobiotic role of AhR in hepatic steatosis.
Methods: Wild-type, constitutively activated AhR transgenic, AhR null and CD36/fatty acid translocase null mice were used to investigate the role of AhR in steatosis and the involvement of CD36 in the steatotic effect of AhR. The promoters of the mouse and human CD36 genes were cloned and their regulation by AhR was analyzed.
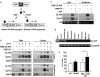
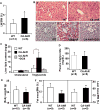
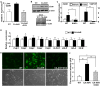
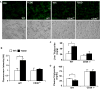
Results: Activation of AhR induced spontaneous hepatic steatosis characterized by the accumulation of triglycerides. The steatotic effect of AhR likely is owing to the combined up-regulation of CD36 and fatty acid transport proteins, suppression of fatty acid oxidation, inhibition of hepatic export of triglycerides, increase in peripheral fat mobilization, and increased hepatic oxidative stress. Promoter analysis established CD36 as a novel transcriptional target of AhR. Activation of AhR in liver cells induced CD36 gene expression and enhanced fatty acid uptake. The steatotic effect of an AhR agonist was inhibited in CD36-/- mice.
Conclusions: Our study reveals a novel link between AhR-induced steatosis and the expression of CD36. Industrial or military exposures to dioxin and related compounds have been linked to increased prevalence of fatty liver in human beings. Results from this study may help to establish AhR and its target CD36 as novel therapeutic and preventive targets for fatty liver disease.
Copyright (c) 2010 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Author conflict of interest disclosures: No conflicts of interest exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor induces hepatic steatosis via the upregulation of fatty acid transport.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010 Dec 15;504(2):221-7. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2010.09.001. Epub 2010 Sep 8. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2010. PMID: 20831858
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor/CD36 pathway to promote hepatic steatosis in mice.Hepatology. 2016 Jul;64(1):92-105. doi: 10.1002/hep.28518. Epub 2016 Apr 5. Hepatology. 2016. PMID: 26928949
-
Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Plays Protective Roles against High Fat Diet (HFD)-induced Hepatic Steatosis and the Subsequent Lipotoxicity via Direct Transcriptional Regulation of Socs3 Gene Expression.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 25;291(13):7004-16. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693655. Epub 2016 Feb 10. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26865635 Free PMC article.
-
The emerging roles of fatty acid translocase/CD36 and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in fatty liver disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011 Oct;236(10):1116-21. doi: 10.1258/ebm.2011.011128. Epub 2011 Sep 1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2011. PMID: 21885479 Review.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: studies using the AHR-null mice.Drug Metab Dispos. 1998 Dec;26(12):1194-8. Drug Metab Dispos. 1998. PMID: 9860927 Review.
Cited by
-
Loss of the Mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase, Tiparp, Increases Sensitivity to Dioxin-induced Steatohepatitis and Lethality.J Biol Chem. 2015 Jul 3;290(27):16824-40. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.660100. Epub 2015 May 13. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25975270 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term in vivo polychlorinated biphenyl 126 exposure induces oxidative stress and alters proteomic profile on islets of Langerhans.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 13;6:27882. doi: 10.1038/srep27882. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27292372 Free PMC article.
-
Lingguizhugan Decoction Protects against High-Fat-Diet-Induced Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Activating Cholesterol Secretion.Int J Genomics. 2017;2017:2790864. doi: 10.1155/2017/2790864. Epub 2017 Dec 31. Int J Genomics. 2017. PMID: 29464180 Free PMC article.
-
AhR and SHP regulate phosphatidylcholine and S-adenosylmethionine levels in the one-carbon cycle.Nat Commun. 2018 Feb 7;9(1):540. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03060-y. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29416063 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell transcriptomics shows dose-dependent disruption of hepatic zonation by TCDD in mice.Toxicol Sci. 2023 Jan 31;191(1):135-148. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfac109. Toxicol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36222588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoffman EC, Reyes H, Chu FF, Sander F, et al. Cloning of a factor required for activity of the Ah (dioxin) receptor. Science. 1991;252:954–958. - PubMed
-
- Reyes H, Reisz-Porszasz S, Hankinson O. Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science. 1992;256:1193–1195. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Salguero PM, Hilbert DM, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, et al. Aryl-hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice are resistant to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced toxicity. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1996;140:173–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

