Fibrocytes in health and disease
- PMID: 20303382
- PMCID: PMC3136351
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.03.004
Fibrocytes in health and disease
Abstract
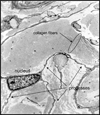
Fibrocytes are circulating mesenchymal progenitor cells that participate in tissue responses to injury and invasion. Accumulating knowledge from animal models regarding the differentiation, trafficking, and function of these cells implicates them in the development of diseases characterized by chronic inflammation and excessive collagen deposition. Recent data obtained from the clinical setting suggests that the enumeration of circulating fibrocytes may be a biomarker for disease progression in chronic lung diseases including asthma and pulmonary fibrosis. A greater understanding of the immunologic mediators that influence fibrocyte biology suggests new opportunities for therapeutic manipulation of these cells in fibrogenesis. This review integrates new developments in the cellular and molecular biology of fibrocytes with current concepts regarding the etiopathogenesis of fibrosing disorders.
Copyright 2010 ISEH - Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Bucala is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Promedior, Inc., which is developing agents to inhibit fibrosis.
Figures
References
-
- Lee CG, Homer RJ, Cohn L, et al. Transgenic overexpression of interleukin (IL)-10 in the lung causes mucus metaplasia, tissue inflammation, and airway remodeling via IL-13-dependent and -independent pathways. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:35466–35474. - PubMed
-
- Noble PW, Homer RJ. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: new insights into pathogenesis. Clin Chest Med. 2004;25:749–758. vii. - PubMed
-
- Liu Y. Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int. 2006;69:213–217. - PubMed
-
- Falk E. Pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2006;47:C7–C12. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources