Interferon-alpha targets JAK2V617F-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells and acts through the p38 MAPK pathway
- PMID: 20303384
- PMCID: PMC4293703
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2010.03.005
Interferon-alpha targets JAK2V617F-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells and acts through the p38 MAPK pathway
Abstract
Objective: Interferon-alpha (IFNalpha) therapy leads to hematological remissions and a reduction of the JAK2V617F allele burden in patients with polycythemia vera (PV). In this study, the cellular target by which IFNalpha affects hematopoiesis in PV patients was evaluated.
Materials and methods: CD34(+) cells were isolated from normal bone marrow and the peripheral blood of patients with PV and were treated in vitro with each of the three commercially available forms of IFNalpha: IFNalpha 2b, pegylated IFNalpha 2a (Peg-IFNalpha 2a), and pegylated IFNalpha 2b (Peg-IFNalpha 2b).
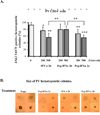
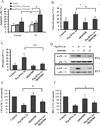
Results: Each form of IFNalpha was equally potent in suppressing hematopoietic colony formation by normal CD34(+) cells, but Peg-IFNalpha 2a and IFNalpha 2b were more effective than Peg-IFNalpha 2b in inhibiting burst-forming unit erythroid-derived colony formation by PV CD34(+) cells. In addition, exposure of PV CD34(+) cells to equal doses of Peg-IFNalpha 2a and IFNalpha 2b resulted in a 38% to 40% reduction in the proportion of JAK2V617F-positive hematopoietic progenitor cells (HPC), while equivalent doses of Peg-IFNalpha 2b did not reduce the number of malignant HPC. Further studies explored the mechanism by which IFNalpha induced PV HPC growth inhibition. Treatment of Peg-IFNalpha 2a increased the rate of apoptosis of PV CD34(+) cells and the phosphorylation/activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in PV CD34(+) cells, while the p38-specific inhibitor SB203580 reversed the growth inhibition and apoptosis induced by Peg-IFNalpha 2a.
Conclusion: These data suggest that low doses of IFNalpha selectively and directly suppress PV JAK2V617F HPC and that these agents act through the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway.
Copyright 2010 ISEH - Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Combination treatment in vitro with Nutlin, a small-molecule antagonist of MDM2, and pegylated interferon-α 2a specifically targets JAK2V617F-positive polycythemia vera cells.Blood. 2012 Oct 11;120(15):3098-105. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-410712. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22872685 Free PMC article.
-
The orally bioavailable MDM2 antagonist RG7112 and pegylated interferon α 2a target JAK2V617F-positive progenitor and stem cells.Blood. 2014 Jul 31;124(5):771-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-536854. Epub 2014 May 28. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24869939 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment with the Bcl-xL inhibitor ABT-737 in combination with interferon α specifically targets JAK2V617F-positive polycythemia vera hematopoietic progenitor cells.Blood. 2010 Nov 18;116(20):4284-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-279125. Epub 2010 Jul 12. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20625010 Free PMC article.
-
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway and its role in interferon signaling.Pharmacol Ther. 2003 May;98(2):129-42. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(03)00016-0. Pharmacol Ther. 2003. PMID: 12725866 Review.
-
Distinct gene expression pattern of malignant hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells in polycythemia vera.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Jun;1044:94-108. doi: 10.1196/annals.1349.013. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 15958702 Review.
Cited by
-
Combination treatment in vitro with Nutlin, a small-molecule antagonist of MDM2, and pegylated interferon-α 2a specifically targets JAK2V617F-positive polycythemia vera cells.Blood. 2012 Oct 11;120(15):3098-105. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-02-410712. Epub 2012 Aug 7. Blood. 2012. PMID: 22872685 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of a signaling feedback circuit that defines interferon responses in myeloproliferative neoplasms.Nat Commun. 2022 Apr 1;13(1):1750. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29381-7. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35365653 Free PMC article.
-
Type I interferon suppresses tumor growth through activating the STAT3-granzyme B pathway in tumor-infiltrating cytotoxic T lymphocytes.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Jun 22;7(1):157. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0635-8. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31228946 Free PMC article.
-
Novel and emerging therapies for the treatment of polycythemia vera.Expert Rev Hematol. 2015 Feb;8(1):101-13. doi: 10.1586/17474086.2015.972359. Epub 2014 Oct 29. Expert Rev Hematol. 2015. PMID: 25353086 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The orally bioavailable MDM2 antagonist RG7112 and pegylated interferon α 2a target JAK2V617F-positive progenitor and stem cells.Blood. 2014 Jul 31;124(5):771-9. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-536854. Epub 2014 May 28. Blood. 2014. PMID: 24869939 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature. 2005;434:1144–1148. - PubMed
-
- Kralovics R, Teo SS, Buser AS, et al. Altered gene expression in myeloproliferative disorders correlates with activation of signaling by the V617F mutation of Jak2. Blood. 2005;106:3374–3376. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Gilliland DG. JAK-2 mutations and their relevance to myeloproliferative disease. Curr Opin Hematol. 2007;14:43–47. - PubMed
-
- Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, et al. Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell. 2005;7:387–397. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Casadevall N, Constantinescu SN, Vainchenker W. A JAK2 mutation in myeloproliferative disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic and scientific prospects. Trends Mol Med. 2005;11:546–554. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

