The point mutation gamma 2F77I changes the potency and efficacy of benzodiazepine site ligands in different GABAA receptor subtypes
- PMID: 20303942
- PMCID: PMC7615656
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.03.015
The point mutation gamma 2F77I changes the potency and efficacy of benzodiazepine site ligands in different GABAA receptor subtypes
Abstract
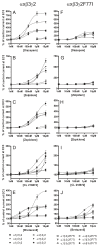
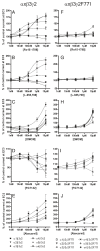
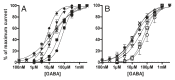
Benzodiazepine site agonists or inverse agonists enhance or reduce gamma-aminobutyric acid(A) (GABA(A)) receptor-mediated inhibition of neurons, respectively. Recently, it was demonstrated that the point mutation gamma 2F77I causes a drastic change in the affinity of a variety of benzodiazepine agonists or inverse agonists in receptor binding studies. Here we investigated the potency and efficacy of 10 benzodiazepine site ligands from 6 structural classes in wild-type and gamma 2F77I point mutated recombinant GABA(A) receptors composed of alpha 1 beta 3 gamma 2, alpha 2 beta 3 gamma 2, alpha 3 beta 3 gamma 2, alpha 4 beta 3 gamma 2, alpha 5 beta 3 gamma 2, and alpha 6 beta 3 gamma 2 subunits. Results indicate that the effects of the benzodiazepine site ligands zolpidem, zopiclone, Cl218872, L-655,708 and DMCM were nearly completely eliminated in all mutated receptors up to a 1 microM concentration. The effects of bretazenil, Ro15-1788 or abecarnil were eliminated in some, but not all mutated receptors, suggesting that the gamma 2F77I mutation differentially influences the actions of these ligands in different receptor subtypes. In addition, this point mutation also influences the efficacy of diazepam for enhancing GABA-induced chloride flux, suggesting that the amino acid residue gamma 2F77 might also be involved in the transduction of the effect of benzodiazepines from binding to gating. The application of these drugs in a novel mouse model is discussed.
(c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of the histidine residue at position 105 in the human alpha 5 containing GABA(A) receptor on the affinity and efficacy of benzodiazepine site ligands.Br J Pharmacol. 2002 Jan;135(1):248-56. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704459. Br J Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11786501 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of two GABAA receptor benzodiazepine-site ligands that are mediated via non-γ2-dependent modulation.Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;666(1-3):111-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.011. Epub 2011 May 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21616065
-
Pharmacology of the human gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor alpha 4 subunit expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes.Mol Pharmacol. 1996 Nov;50(5):1364-75. Mol Pharmacol. 1996. PMID: 8913369
-
A closer look at the high affinity benzodiazepine binding site on GABAA receptors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11(2):241-6. doi: 10.2174/156802611794863562. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011. PMID: 21189125 Review.
-
Mapping of the benzodiazepine recognition site on GABA(A) receptors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2002 Aug;2(8):833-9. doi: 10.2174/1568026023393444. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12171574 Review.
Cited by
-
Ester to amide substitution improves selectivity, efficacy and kinetic behavior of a benzodiazepine positive modulator of GABAA receptors containing the α5 subunit.Eur J Pharmacol. 2016 Nov 15;791:433-443. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.09.016. Epub 2016 Sep 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27639297 Free PMC article.
-
Subtype selectivity of α+β- site ligands of GABAA receptors: identification of the first highly specific positive modulators at α6β2/3γ2 receptors.Br J Pharmacol. 2013 May;169(2):384-99. doi: 10.1111/bph.12153. Br J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23472935 Free PMC article.
-
Cryo-EM structures reveal native GABAA receptor assemblies and pharmacology.Nature. 2023 Oct;622(7981):195-201. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06556-w. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Nature. 2023. PMID: 37730991 Free PMC article.
-
Negative modulation of α₅ GABAA receptors in rats may partially prevent memory impairment induced by MK-801, but not amphetamine- or MK-801-elicited hyperlocomotion.J Psychopharmacol. 2015 Sep;29(9):1013-24. doi: 10.1177/0269881115590601. Epub 2015 Jun 23. J Psychopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26105958 Free PMC article.
-
Benzodiazepine-induced spatial learning deficits in rats are regulated by the degree of modulation of α1 GABA(A) receptors.Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013 May;23(5):390-9. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2012.05.003. Epub 2012 May 26. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 22633616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Atack JR. Anxioselective compounds acting at the GABA(A) receptor benzodiazepine binding site. Curr Drug Targets. 2003;2:213–232. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Bayley PJ, Seabrook GR, Wafford KA, McKernan RM, Dawson GR. L-655,708 enhances cognition in rats but is not proconvulsant at a dose selective for alpha5-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropharmacology. 2006;51:1023–1029. - PubMed
-
- Atack JR, Maubach KA, Wafford KA, O’Connor D, Rodrigues AD, Evans DC, Tattersall FD, Chambers MS, MacLeod AM, Eng WS, Ryan C, et al. In vitro and in vivo properties of 3-tert-butyl-7-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)-2-(1-methyl-1H-1,2,4-triazol-5-ylme thoxy)-pyrazolo[1,5-d]-[1,2,4]triazine (MRK-016), a GABAA receptor alpha5 subtype-selective inverse agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;331:470–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

