Three-dimensional analysis of tumour vascular corrosion casts using stereoimaging and micro-computed tomography
- PMID: 20303995
- PMCID: PMC4398341
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mvr.2010.03.007
Three-dimensional analysis of tumour vascular corrosion casts using stereoimaging and micro-computed tomography
Abstract
Objective: In order to perform effective translational research for cancer therapy, we need to employ pre-clinical models which reflect the clinical situation. The purpose of this study was to quantitatively compare the vascular architecture of human colorectal cancer and experimental tumour models to determine the suitability of animal models for vascular studies and antivascular therapy.
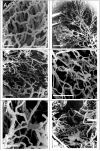
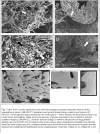
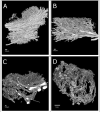
Methods: In this study we investigated the three-dimensional properties of colonic tumour vasculature in both human clinical tissues (normal mucosa control [n=20], carcinoma [n=20] and adenoma [n=6]) and murine colorectal xenografts (LS147T [n=6] and SW1222 [n=6]). Scanning Electron Microscope Stereoimaging (SEM) and X-ray Micro-Computed Tomography (Micro-CT) methods were employed for 3D analyses of the vascular corrosion casts from these tissues.
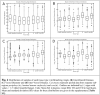
Results: Morphological measurements showed that there were significant differences in the underlying morphology in the different tissues. Of the studied xenografts, LS147T is more consistently similar to the vascular architecture of the human carcinoma than SW1222. The only reversal of this is for the inter-vessel distance.
Conclusion: While SEM stereoimaging provided better surface detailed resolution of the corrosion casts, it was complimented by the fully 3D micro-CT method. Comparison made between the xenografts and clinical tumours showed that the LS147T xenografts shared many similarities with the clinical tumour vasculature. This study provides insight into how to select the most suitable pre-clinical models for translational studies of clinical cancer therapy.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
MRI measurements of vessel calibre in tumour xenografts: comparison with vascular corrosion casting.Microvasc Res. 2012 Nov;84(3):323-9. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2012.08.001. Epub 2012 Aug 18. Microvasc Res. 2012. PMID: 22921880 Free PMC article.
-
Imaging angiogenesis: perspectives and opportunities in tumour research - a method display.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014 Sep;42(6):915-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 14. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014. PMID: 24518362
-
Evidence for characteristic vascular patterns in solid tumours: quantitative studies using corrosion casts.Br J Cancer. 1999 May;80(5-6):724-32. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6690416. Br J Cancer. 1999. PMID: 10360650 Free PMC article.
-
Scanning electron microscopy of vascular corrosion casts--standard method for studying microvessels.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2007;48(3):257-61. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2007. PMID: 17914492 Review.
-
Hierarchical imaging and computational analysis of three-dimensional vascular network architecture in the entire postnatal and adult mouse brain.Nat Protoc. 2021 Oct;16(10):4564-4610. doi: 10.1038/s41596-021-00587-1. Epub 2021 Sep 3. Nat Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34480130 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel in vivo vascular imaging approach for hierarchical quantification of vasculature using contrast enhanced micro-computed tomography.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86562. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086562. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475146 Free PMC article.
-
Dissemination from a Solid Tumor: Examining the Multiple Parallel Pathways.Trends Cancer. 2018 Jan;4(1):20-37. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.12.002. Epub 2018 Jan 10. Trends Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29413419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Texture analysis of (125)I-A5B7 anti-CEA antibody SPECT differentiates metastatic colorectal cancer model phenotypes and anti-vascular therapy response.Br J Cancer. 2015 Jun 9;112(12):1882-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.166. Epub 2015 May 19. Br J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25989271 Free PMC article.
-
Building an experimental model of the human body with non-physiological parameters.Technology (Singap World Sci). 2017 Mar;5(1):42-59. doi: 10.1142/S2339547817500029. Epub 2017 Mar 31. Technology (Singap World Sci). 2017. PMID: 28713851 Free PMC article.
-
A perspective on vascular disrupting agents that interact with tubulin: preclinical tumor imaging and biological assessment.Integr Biol (Camb). 2011 Apr;3(4):375-87. doi: 10.1039/c0ib00135j. Epub 2011 Feb 14. Integr Biol (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21321746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Belien JA, van Diest PJ, Baak JP. Relationships between vascularization and proliferation in invasive breast cancer. J. Pathol. 1999;189:309–318. - PubMed
-
- Bentley MD, Ortiz MC, Ritman EL, Romero JC. The use of microcomputed tomography to study microvasculature in small rodents. Am. J. Physiol Regul. Integr. Comp Physiol. 2002;282:R1267–R1279. - PubMed
-
- Bidiwala SB, Mansour MS, Stengel CK, Klein SA, Carroll SM, Koenig SC, Desoky AH, Tobin GR, Maldonado C, Barker JH. Quantification of the morphological features of a full microvascular network. Med. Biol. Eng Comput. 1998;36:621–626. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

