Detection of nitric oxide by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy
- PMID: 20304044
- PMCID: PMC2916063
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2010.03.009
Detection of nitric oxide by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy
Abstract
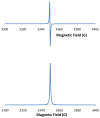
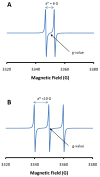
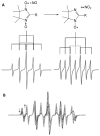
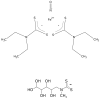
Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectroscopy has been used in a number of ways to study nitric oxide chemistry and biology. As an intrinsically stable and relatively unreactive diatomic free radical, the challenges of detecting this species by EPR are somewhat different from those of transient radical species. This review gives a basic introduction to EPR spectroscopy and discusses its uses to assess and quantify nitric oxide formation in biological systems.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
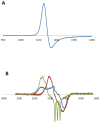
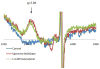
References
-
- Duling DR. Simulation of multiple isotropic spin-trap EPR spectra. J Magn Res B. 1994;104:105–110. - PubMed
-
- Knowles PF, March D, Rattle HWE. Magnetic Resonance of Biomolecules. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons; 1976.
-
- Weil JA, Bolton JR. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Elementary Theory and Practical Applications. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons; 2007.
-
- Uehara H, Arimitsu S. Gas-phase electron paramagnetic resonance detection of ntiric oxide and nitrogen dioxide in pulluted air. Anal Chem. 1973;45:1897–1900. - PubMed
-
- Villamena FA, Zweier JL. Detection of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species by EPR Spin Trapping. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling. 2004;6:619–629. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

