Interactions between declarative and procedural-learning categorization systems
- PMID: 20304078
- PMCID: PMC2881184
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.03.001
Interactions between declarative and procedural-learning categorization systems
Abstract
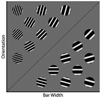
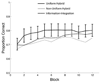
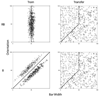
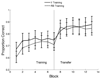
Two experiments tested whether declarative and procedural memory systems operate independently or inhibit each other during perceptual categorization. Both experiments used a hybrid category-learning task in which perfect accuracy could be achieved if a declarative strategy is used on some trials and a procedural strategy is used on others. In the two experiments, only 2 of 53 participants learned a strategy of this type. In Experiment 1, most participants appeared to use simple explicit rules, even though control participants reliably learned the procedural component of the hybrid task. In Experiment 2, participants pre-trained either with the declarative or procedural component and then transferred to the hybrid categories. Despite this extra training, no participants in either group learned to categorize the hybrid stimuli with a strategy of the optimal type. These results are inconsistent with the most prominent single- and multiple-system accounts of category learning. They also cannot be explained by knowledge partitioning, or by the hypothesis that the failure to learn was due to high switch costs. Instead, these results support the hypothesis that declarative and procedural memory systems interact during category learning.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Trial-by-trial switching between procedural and declarative categorization systems.Psychol Res. 2018 Mar;82(2):371-384. doi: 10.1007/s00426-016-0828-4. Epub 2016 Nov 30. Psychol Res. 2018. PMID: 27900481 Free PMC article.
-
Procedural-Memory, Working-Memory, and Declarative-Memory Skills Are Each Associated With Dimensional Integration in Sound-Category Learning.Front Psychol. 2018 Oct 2;9:1828. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01828. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30333772 Free PMC article.
-
Declarative strategies persist under increased cognitive load.Psychon Bull Rev. 2016 Feb;23(1):213-22. doi: 10.3758/s13423-015-0867-7. Psychon Bull Rev. 2016. PMID: 26160426 Free PMC article.
-
The declarative/procedural model of lexicon and grammar.J Psycholinguist Res. 2001 Jan;30(1):37-69. doi: 10.1023/a:1005204207369. J Psycholinguist Res. 2001. PMID: 11291183 Review.
-
The connection between the hippocampal and the striatal memory systems of the brain: a review of recent findings.Neurotox Res. 2006 Oct;10(2):113-21. doi: 10.1007/BF03033240. Neurotox Res. 2006. PMID: 17062373 Review.
Cited by
-
Erasing the engram: the unlearning of procedural skills.J Exp Psychol Gen. 2013 Aug;142(3):710-41. doi: 10.1037/a0030059. Epub 2012 Oct 8. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2013. PMID: 23046090 Free PMC article.
-
Feedback and stimulus-offset timing effects in perceptual category learning.Brain Cogn. 2013 Mar;81(2):283-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bandc.2012.11.006. Epub 2013 Jan 9. Brain Cogn. 2013. PMID: 23313835 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Categorization system-switching deficits in typical aging and Parkinson's disease.Neuropsychology. 2018 Sep;32(6):724-734. doi: 10.1037/neu0000459. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Neuropsychology. 2018. PMID: 29952585 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical and striatal contributions to automaticity in information-integration categorization.Neuroimage. 2011 Jun 1;56(3):1791-802. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.02.011. Epub 2011 Feb 18. Neuroimage. 2011. PMID: 21316475 Free PMC article.
-
Theory of Mind Deficit versus Faulty Procedural Memory in Autism Spectrum Disorders.Autism Res Treat. 2013;2013:128264. doi: 10.1155/2013/128264. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Autism Res Treat. 2013. PMID: 23862063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ashby FG. Multidimensional models of categorization. In: Ashby FG, editor. Multidimensional models of perception and cognition. Hillsdale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, Inc.; 1992. pp. 449–483.
-
- Ashby FG, Alfonso-Reese L. Categorization as probability density estimation. Journal of Mathematical Psychology. 1995;39:216–233.
-
- Ashby FG, Alfonso-Reese LA, Turken AU, Waldron EM. A neuropsychological theory of multiple systems in category learning. Psychological Review. 1998;105:442–481. - PubMed
-
- Ashby FG, Ell SW, Waldron EM. Procedural learning in perceptual categorization. Memory & Cognition. 2003;31:1114–1125. - PubMed
-
- Ashby FG, Gott RE. Decision rules in the perception and categorization of multidimensional stimuli. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory and cognition. 1988;14:33–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

