Synergistic effects of tethered growth factors and adhesion ligands on DNA synthesis and function of primary hepatocytes cultured on soft synthetic hydrogels
- PMID: 20304480
- PMCID: PMC2872479
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.01.138
Synergistic effects of tethered growth factors and adhesion ligands on DNA synthesis and function of primary hepatocytes cultured on soft synthetic hydrogels
Abstract
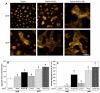
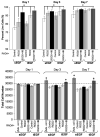
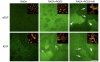
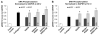
The composition, presentation, and spatial orientation of extracellular matrix molecules and growth factors are key regulators of cell behavior. Here, we used self-assembling peptide nanofiber gels as a modular scaffold to investigate how fibronectin-derived adhesion ligands and different modes of epidermal growth factor (EGF) presentation synergistically regulate multiple facets of primary rat hepatocyte behavior in the context of a soft gel. In the presence of soluble EGF, inclusion of dimeric RGD and the heparin binding domain from fibronectin (HB) increased hepatocyte aggregation, spreading, and metabolic function compared to unmodified gels or gels modified with a single motif, but unlike rigid substrates, gels failed to induce DNA synthesis. Tethered EGF dramatically stimulated cell aggregation and spreading under all adhesive ligand conditions and also preserved metabolic function. Surprisingly, tethered EGF elicited DNA synthesis on gels with RGD and HB. Phenotypic differences between soluble and tethered EGF stimulation of cells on peptide gels are correlated with differences in expression and phosphorylation the EGF receptor and its heterodimerization partner ErbB2, and activation of the downstream signaling node ERK1/2. These modular matrices reveal new facets of hepatocellular biology in culture and may be more broadly useful in culture of other soft tissues.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology in vitro. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7(3):211–24. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

