Genetic variants and risk of lung cancer in never smokers: a genome-wide association study
- PMID: 20304703
- PMCID: PMC2945218
- DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70042-5
Genetic variants and risk of lung cancer in never smokers: a genome-wide association study
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer in individuals who have never smoked tobacco products is an increasing medical and public-health issue. We aimed to unravel the genetic basis of lung cancer in never smokers.
Methods: We did a four-stage investigation. First, a genome-wide association study of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was done with 754 never smokers (377 matched case-control pairs at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN, USA). Second, the top candidate SNPs from the first study were validated in two independent studies among 735 (MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, TX, USA) and 253 (Harvard University, Boston, MA, USA) never smokers. Third, further replication of the top SNP was done in 530 never smokers (UCLA, Los Angeles, CA, USA). Fourth, expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) and gene-expression differences were analysed to further elucidate the causal relation between the validated SNPs and the risk of lung cancer in never smokers.
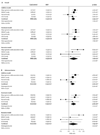
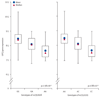
Findings: 44 top candidate SNPs were identified that might alter the risk of lung cancer in never smokers. rs2352028 at chromosome 13q31.3 was subsequently replicated with an additive genetic model in the four independent studies, with a combined odds ratio of 1.46 (95% CI 1.26-1.70, p=5.94x10(-6)). A cis eQTL analysis showed there was a strong correlation between genotypes of the replicated SNPs and the transcription level of the gene GPC5 in normal lung tissues (p=1.96x10(-4)), with the high-risk allele linked with lower expression. Additionally, the transcription level of GPC5 in normal lung tissue was twice that detected in matched lung adenocarcinoma tissue (p=6.75x10(-11)).
Interpretation: Genetic variants at 13q31.3 alter the expression of GPC5, and are associated with susceptibility to lung cancer in never smokers. Downregulation of GPC5 might contribute to the development of lung cancer in never smokers.
Funding: US National Institutes of Health; Mayo Foundation.
2010 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Lung cancer in never smokers: a new hot area of research.Lancet Oncol. 2010 Apr;11(4):304-5. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70057-7. Epub 2010 Mar 19. Lancet Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20304702 No abstract available.
-
GPC5 rs2352028 variant and risk of lung cancer in never smokers.Lancet Oncol. 2010 Aug;11(8):714-6; author reply 716. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70096-6. Lancet Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20688270 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
GPC5 and lung cancer in multiple sclerosis.Lancet Oncol. 2010 Aug;11(8):714. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(10)70177-7. Lancet Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20688271 No abstract available.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Sun S, Schiller JH, Gazdar AF. Lung cancer in never smokers—a different disease. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:778–790. - PubMed
-
- Subramanian J, Govindan R. Lung cancer in never smokers: a review. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:561–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P20 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA09142/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092824/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA127615/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084354/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA80127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA009142/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA074386/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA90833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA111646/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA090578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA111646/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA090833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA055769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA096520/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA127615/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA092824/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA074386/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA84354/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA080127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA070907/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA BC005480/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

