Specific estrogen sulfotransferase (SULT1E1) substrates and molecular imaging probe candidates
- PMID: 20304798
- PMCID: PMC2852016
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0914904107
Specific estrogen sulfotransferase (SULT1E1) substrates and molecular imaging probe candidates
Abstract
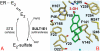
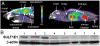
This work focuses on the development of specific substrates for estrogen sulfotransferase (SULT1E1) to produce molecular imaging probes for this enzyme. SULT1E1 is a key enzyme in estrogen homeostasis, playing a central role in the prevention and development of human disease. In vitro sulfation assays showed alkyl and aryl substitutions to a fused heterocyclic system modeled after beta-naphthol (betaN), based on compounds that interact with the estrogen receptor, rendered several molecules with enhanced specificity for SULT1E1 over SULT1A1*1, SULT1A1*2, SULT1A3, and SULT2A1. Several 6-hydroxy-2-arylbenzothiazoles tested demonstrated excellent affinity--V(max)/K(m) ratios-and specificity for SULT1E1. K(m) values ranged from 0.12-2.36 microM. A strong correlation was observed between polarity of the 4'-sustituent on the 2-aryl moiety (Hammett sigma(p)) and the log(V(max)/K(m)) (r = 0.964). Substrate sensitivity is influenced by the acidity of the 6-phenolic group demonstrated by correlating its (1)H NMR chemical shift (delta(OH)) with the log(V(max)/K(m)) (r = 0.963). Acidity is mediated by the electron withdrawing capacity of the 4'-substituent outlined by the correlation of the C-2 (13)C NMR chemical shift (delta(C2)) with the log(V(max)/K(m)) (r = 0.987). 2-[4-(Methylamino)phenyl]-6-hydroxybenzothiazole (2b) was radiolabeled with carbon-11 ((11)C-(2b)) and used in vivo for microPET scanning and tissue metabolite identification. High PET signal was paralleled with the presence of radiolabeled (11)C-(2b)-6-O-sulfate and the SULT1E1 protein detected by western blot. Because this and other members of this family presenting specificity for SULT1E1 can be labeled with carbon-11 or fluorine-18, in vivo assays of SULT1E1 functional activity are now feasible in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
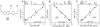


Similar articles
-
Expression and functional activities of selected sulfotransferase isoforms in BeWo cells and primary cytotrophoblast cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2009 Dec 15;78(12):1475-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.07.013. Epub 2009 Jul 30. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19646966 Free PMC article.
-
Regioselective monosulfation and disulfation of the phytoestrogens daidzein and genistein by human liver sulfotransferases.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2004 Jun;19(3):216-26. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.19.216. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2004. PMID: 15499189
-
Sulfation of environmental estrogens by cytosolic human sulfotransferases.Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2002;17(3):221-8. doi: 10.2133/dmpk.17.221. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2002. PMID: 15618673
-
Estrogen sulfotransferase in the metabolism of estrogenic drugs and in the pathogenesis of diseases.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019 Apr;15(4):329-339. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2019.1588884. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30822161 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions of cytosolic sulfotransferases with xenobiotics.Drug Metab Rev. 2013 Nov;45(4):401-14. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2013.835613. Drug Metab Rev. 2013. PMID: 24188364 Review.
Cited by
-
Probing predilection to Crohn's disease and Crohn's disease flares: A crowd-sourced bioinformatics approach.J Pathol Inform. 2022 May 1;13:100094. doi: 10.1016/j.jpi.2022.100094. eCollection 2022. J Pathol Inform. 2022. PMID: 36268056 Free PMC article.
-
[F-18]FDDNP microPET imaging correlates with brain Aβ burden in a transgenic rat model of Alzheimer disease: effects of aging, in vivo blockade, and anti-Aβ antibody treatment.Neurobiol Dis. 2011 Sep;43(3):565-75. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.05.003. Epub 2011 May 13. Neurobiol Dis. 2011. PMID: 21605674 Free PMC article.
-
Small-molecule PET Tracers for Imaging Proteinopathies.Semin Nucl Med. 2017 Sep;47(5):553-575. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2017.06.003. Epub 2017 Jul 13. Semin Nucl Med. 2017. PMID: 28826526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Depressive and anxiety symptoms and cortical amyloid deposition among cognitively normal elderly persons: the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging.Int Psychogeriatr. 2018 Feb;30(2):245-251. doi: 10.1017/S1041610217002368. Epub 2017 Dec 4. Int Psychogeriatr. 2018. PMID: 29198244 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of brain amyloid with "aerobic glycolysis": A question of assumptions?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Oct 12;107(41):17459-60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012684107. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20921385 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Falany C. Enzymology of human cytosolic sulfotransferases. FASEB J. 1997;11(4):206–216. - PubMed
-
- Blanchard RL. Human cytosolic sulfotransferases. In: Pacifici GM, Coughtrie MWH, editors. Boca Raton, FL: Taylor and Francis Group, LLC; 2005. pp. 1–8.
-
- Miki Y, et al. Systemic distribution of steroid sulfatase and estrogen sulfotransferase in human adult and fetal tissues. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2002;87(12):5760–5768. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H, Varmalova O, Vargas FM, Falany CN, Leyh TS. Sulfuryl transfer: The catalytic mechanism of human estrogen sulfotransferase. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(18):10888–10892. - PubMed
-
- Syed F, Khosla S. Mechanisms of sex steroid effects on bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;328:688–696. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

