Distribution and function of macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 2 (MGL2/CD301b): efficient uptake and presentation of glycosylated antigens by dendritic cells
- PMID: 20304916
- PMCID: PMC2885198
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.113613
Distribution and function of macrophage galactose-type C-type lectin 2 (MGL2/CD301b): efficient uptake and presentation of glycosylated antigens by dendritic cells
Abstract
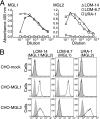
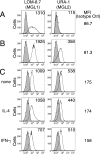
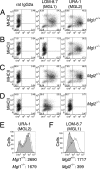
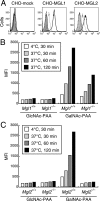
Dendritic cells (DCs) express cell surface lectins that are potentially involved in the recognition, uptake, and presentation of glycosylated foreign substances. A unique calcium-type (C-type) lectin, the macrophage galactose (Gal)-type C-type lectin (MGL/CD301) expressed on DCs, is thought to participate in the recognition of molecules from both altered self and pathogens due to its monosaccharide specificity for Gal and N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc). Although mice have two MGL genes, Mgl1 and Mgl2, their distinct roles have not been previously explored. The present report characterizes the properties of MGL2 by examining its distribution and its role in antigen presentation by DCs. We generated an MGL2-specific monoclonal antibody and examined MGL2 expression in tissues by immunohistochemistry and in isolated cells by flow cytometry. The cells reactive with this antibody were shown to be a portion of MGL1-expressing cells, mostly conventional DCs. Internalization of soluble polyacrylamide polymers (PAA) with alpha-GalNAc residues (GalNAc-PAA) by bone marrow-derived DCs (BM-DCs) was mediated by MGL2, as revealed by a comparison of Mgl1(-/-) and Mgl2(-/-) BM-DCs with wild-type BM-DCs. Biotinylated GalNAc-PAA conjugated to streptavidin (SAv) was more efficiently presented to SAv-primed T cells by BM-DCs than beta-N-acetylglucosamine-PAA conjugated to SAv or SAv alone as shown by thymidine uptake and cytokine production. This is the first report that demonstrates the involvement of GalNAc residues in antigen uptake and presentation by DCs that lead to CD4(+) T cell activation.
Figures



References
-
- Apweiler R., Hermjakob H., Sharon N. (1999) Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1473, 4–8 - PubMed
-
- Banchereau J., Steinman R. M. (1998) Nature 392, 245–252 - PubMed
-
- Cambi A., Figdor C. G. (2003) Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 539–546 - PubMed
-
- Figdor C. G., van Kooyk Y., Adema G. J. (2002) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2, 77–84 - PubMed
-
- Robinson M. J., Sancho D., Slack E. C., LeibundGut-Landmann S., Reis e Sousa C. (2006) Nat. Immunol. 7, 1258–1265 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

