The signal peptide of the IgE receptor alpha-chain prevents surface expression of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-free receptor pool
- PMID: 20304923
- PMCID: PMC2865261
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.104281
The signal peptide of the IgE receptor alpha-chain prevents surface expression of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-free receptor pool
Abstract
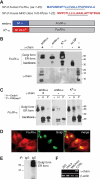
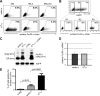
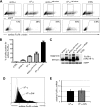
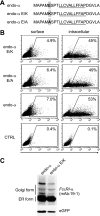
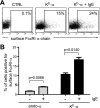
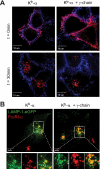
The high affinity receptor for IgE, Fc epsilon receptor I (FcepsilonRI), is an activating immune receptor and key regulator of allergy. Antigen-mediated cross-linking of IgE-loaded FcepsilonRI alpha-chains induces cell activation via immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motifs in associated signaling subunits, such as FcepsilonRI gamma-chains. Here we show that the human FcepsilonRI alpha-chain can efficiently reach the cell surface by itself as an IgE-binding receptor in the absence of associated signaling subunits when the endogenous signal peptide is swapped for that of murine major histocompatibility complex class-I H2-K(b). This single-chain isoform of FcepsilonRI exited the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), trafficked to the Golgi and, subsequently, trafficked to the cell surface. Mutational analysis showed that the signal peptide regulates surface expression in concert with other described ER retention signals of FcepsilonRI-alpha. Once the FcepsilonRI alpha-chain reached the cell surface by itself, it formed a ligand-binding receptor that stabilized upon IgE contact. Independently of the FcepsilonRI gamma-chain, this single-chain FcepsilonRI was internalized after receptor cross-linking and trafficked into a LAMP-1-positive lysosomal compartment like multimeric FcepsilonRI. These data suggest that the single-chain isoform is capable of shuttling IgE-antigen complexes into antigen loading compartments, which plays an important physiologic role in the initiation of immune responses toward allergens. We propose that, in addition to cytosolic and transmembrane ER retention signals, the FcepsilonRI alpha-chain signal peptide contains a negative regulatory signal that prevents expression of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif-free IgE receptor pool, which would fail to induce cell activation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transport of the IgE receptor alpha-chain is controlled by a multicomponent intracellular retention signal.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 14;281(15):10448-60. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M510751200. Epub 2006 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16459334
-
Export of the high affinity IgE receptor from the endoplasmic reticulum depends on a glycosylation-mediated quality control mechanism.J Immunol. 2000 Nov 15;165(10):5686-94. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.10.5686. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11067926
-
Downstream signaling molecules bind to different phosphorylated immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM) peptides of the high affinity IgE receptor.J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 1;271(44):27962-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.44.27962. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8910399
-
Regulation of Trafficking and Signaling of the High Affinity IgE Receptor by FcεRIβ and the Potential Impact of FcεRIβ Splicing in Allergic Inflammation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 12;23(2):788. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020788. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights into the interactions between human IgE and its high affinity receptor FcepsilonRI.Mol Immunol. 2002 May;38(14):1063-72. doi: 10.1016/s0161-5890(02)00035-4. Mol Immunol. 2002. PMID: 11955598 Review.
Cited by
-
Cloning and characterization of CD300d, a novel member of the human CD300 family of immune receptors.J Biol Chem. 2012 Mar 23;287(13):9682-9693. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.279224. Epub 2012 Jan 30. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 22291008 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative reactivity of human IgE to cynomolgus monkey and human effector cells and effects on IgE effector cell potency.MAbs. 2014 Mar-Apr;6(2):509-22. doi: 10.4161/mabs.27828. Epub 2014 Jan 14. MAbs. 2014. PMID: 24492303 Free PMC article.
-
Functions of dendritic-cell-bound IgE in allergy.Mol Immunol. 2015 Dec;68(2 Pt A):116-9. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.05.016. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26052071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD33 recruitment inhibits IgE-mediated anaphylaxis and desensitizes mast cells to allergen.J Clin Invest. 2019 Mar 1;129(3):1387-1401. doi: 10.1172/JCI125456. Epub 2019 Feb 18. J Clin Invest. 2019. PMID: 30645205 Free PMC article.
-
A targeted RNAi screen identifies factors affecting diverse stages of receptor-mediated transcytosis.J Cell Biol. 2017 Feb;216(2):511-525. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201609035. Epub 2017 Jan 9. J Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28069747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abramson J., Pecht I. (2007) Immunol. Rev. 217, 231–254 - PubMed
-
- Gould H. J., Sutton B. J. (2008) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8, 205–217 - PubMed
-
- Kraft S., Kinet J. P. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 365–378 - PubMed
-
- Call M. E., Wucherpfennig K. W. (2005) Annu. Rev. Immunol. 23, 101–125 - PubMed
-
- Call M. E., Wucherpfennig K. W. (2007) Nat. Rev. Immunol. 7, 841–850 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

