Subunit arrangement in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors
- PMID: 20304927
- PMCID: PMC2865314
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.085035
Subunit arrangement in N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors
Abstract
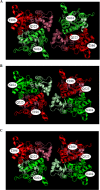
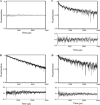
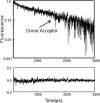
N-Methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, the main mediators of excitatory synaptic transmission, are heterotetrameric receptors. Typically, glycine binding NR1 subunits co-assemble with glutamate binding NR2 subunits to form a functional receptor. Here we have used luminescence resonance energy transfer (LRET) investigations to establish the specific configuration in which these subunits assemble to form the functional tetramer and show that the dimer of dimers structure is formed by the NR1 subunits assembling diagonally to each other. The distances measured by LRET are consistent with the NMDA structure predicted based on cross-linking investigations and on the structure of the full-length alpha-amino-5-methyl-3-hydroxy-4-isoxazole propionic acid (AMPA) receptor structure (1). Additionally, the LRET distances between the NR1 and NR2A subunits within a dimer measured in the desensitized state of the receptor are longer than the distances in the previously published crystal structure of the isolated ligand binding domain of NR1-NR2A. Because the dimer interface in the isolated ligand binding domain crystallizes in the open channel structure, the longer LRET distances would be consistent with the decoupling of the dimer interface in the desensitized state. This is similar to what has been previously observed for the AMPA subtype of the ionotropic glutamate receptors, suggesting a similar mechanism for desensitization in the two subtypes of the glutamate receptor.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Subunit assembly of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors analyzed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer.J Biol Chem. 2005 Jul 1;280(26):24923-30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M413915200. Epub 2005 May 10. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15888440
-
Conformational changes at the agonist binding domain of the N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptor.J Biol Chem. 2011 May 13;286(19):16953-7. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.224576. Epub 2011 Mar 24. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21454656 Free PMC article.
-
Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits.J Biol Chem. 1995 Aug 25;270(34):20036-41. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.34.20036. J Biol Chem. 1995. PMID: 7544350
-
[Structure and function of NMDA-type glutamate receptor subunits].Neurologia. 2012 Jun;27(5):301-10. doi: 10.1016/j.nrl.2011.10.014. Epub 2012 Jan 2. Neurologia. 2012. PMID: 22217527 Review. Spanish.
-
Assembly of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors.Biochem Soc Trans. 2003 Aug;31(Pt 4):865-8. doi: 10.1042/bst0310865. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003. PMID: 12887323 Review.
Cited by
-
Amino-terminal domain tetramer organization and structural effects of zinc binding in the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 2;288(31):22555-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.482356. Epub 2013 Jun 21. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23792960 Free PMC article.
-
Amino terminal domains of the NMDA receptor are organized as local heterodimers.PLoS One. 2011 Apr 22;6(4):e19180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019180. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21544205 Free PMC article.
-
Proton-mediated conformational changes in an acid-sensing ion channel.J Biol Chem. 2013 Dec 13;288(50):35896-903. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.478982. Epub 2013 Nov 6. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24196950 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved structural mechanism of NMDA receptor inhibition: A comparison of ifenprodil and zinc.J Gen Physiol. 2015 Aug;146(2):173-81. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511422. Epub 2015 Jul 13. J Gen Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26170175 Free PMC article.
-
Subtype-dependent N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor amino-terminal domain conformations and modulation by spermine.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 15;290(20):12812-20. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.649723. Epub 2015 Mar 31. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25829490 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hollmann M., O'Shea-Greenfield A., Rogers S. W., Heinemann S. (1989) Nature 342, 643–648 - PubMed
-
- Keinänen K., Wisden W., Sommer B., Werner P., Herb A., Verdoorn T. A., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. (1990) Science 249, 556–560 - PubMed
-
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. (1991) Nature 354, 31–37 - PubMed
-
- Johnson J. W., Ascher P. (1987) Nature 325, 529–531 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

