Therapeutic strategies for targeting excessive central sympathetic activation in human hypertension
- PMID: 20304932
- PMCID: PMC2858400
- DOI: 10.1113/expphysiol.2009.047332
Therapeutic strategies for targeting excessive central sympathetic activation in human hypertension
Abstract
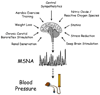
The pathogenesis of hypertension and its mode of progression are complex, multifactoral and incompletely understood. However, there is accumulating evidence from humans and animal models of hypertension indicating that excessive central sympathetic nerve activity (SNA) plays a pathogenic role in triggering and sustaining the essential hypertensive state (the so-called 'neuroadrenergic hypothesis'). Importantly, augmented central sympathetic outflow has also been implicated in the initiation and progression of a plethora of pathophysiological processes independent of any increase in blood pressure, such as left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac arrhythmias. Thus, the sympathetic nervous system constitutes an important putative drug target in hypertension. However, traditional pharmacological approaches for the management of essential hypertension appear ineffective in reducing central sympathetic outflow. Recently, several new and promising therapeutic strategies targeting neurogenic hypertension have been developed. The present report will provide a brief update of this topic with a particular emphasis on human studies examining the efficacy of novel pharmacological approaches (central sympatholytics and statins), lifestyle modification (aerobic exercise training, weight loss and stress reduction) and surgical intervention (renal denervation, chronic carotid baroreflex stimulation and deep brain stimulation) in reducing excessive central sympathetic activation in hypertension.
Figures
References
-
- Ashida T, Ono C, Sugiyama T. Effects of short-term hypocaloric diet on sympatho-vagal interaction assessed by spectral analysis of heart rate and blood pressure variability during stress tests in obese hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res. 2007;30:1199–1203. - PubMed
-
- Bilgutay AM, Lillehei CW. Treatment of Hypertension with an Implantable Electronic Device. JAMA. 1965;191:649–653. - PubMed
-
- Boger RH. The emerging role of asymmetric dimethylarginine as a novel cardiovascular risk factor. Cardiovasc Res. 2003;59:824–833. - PubMed
-
- Brown CD, Higgins M, Donato KA, Rohde FC, Garrison R, Obarzanek E, Ernst ND, Horan M. Body mass index and the prevalence of hypertension and dyslipidemia. Obes Res. 2000;8:605–619. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

