Evidence of localized prophage-host recombination in the lytA gene, encoding the major pneumococcal autolysin
- PMID: 20304992
- PMCID: PMC2863564
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01501-09
Evidence of localized prophage-host recombination in the lytA gene, encoding the major pneumococcal autolysin
Abstract
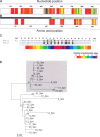
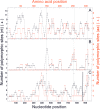
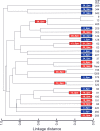
According to a highly polymorphic region in the lytA gene, encoding the major autolysin of Streptococcus pneumoniae, two different families of alleles can be differentiated by PCR and restriction digestion. Here, we provide evidence that this polymorphic region arose from recombination events with homologous genes of pneumococcal temperate phages.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae: a Plethora of Temperate Bacteriophages With a Role in Host Genome Rearrangement.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 18;11:775402. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.775402. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34869076 Free PMC article.
-
The autolysin-encoding gene (lytA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae displays restricted allelic variation despite localized recombination events with genes of pneumococcal bacteriophage encoding cell wall lytic enzymes.Infect Immun. 1999 Sep;67(9):4551-6. doi: 10.1128/IAI.67.9.4551-4556.1999. Infect Immun. 1999. PMID: 10456899 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of LytA-like N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidases from two new Streptococcus mitis bacteriophages provides insights into the properties of the major pneumococcal autolysin.J Bacteriol. 2004 Dec;186(24):8229-39. doi: 10.1128/JB.186.24.8229-8239.2004. J Bacteriol. 2004. PMID: 15576771 Free PMC article.
-
The pneumococcal cell wall degrading enzymes: a modular design to create new lysins?Microb Drug Resist. 1997 Summer;3(2):199-211. doi: 10.1089/mdr.1997.3.199. Microb Drug Resist. 1997. PMID: 9185148 Review.
-
Biological roles of two new murein hydrolases of Streptococcus pneumoniae representing examples of module shuffling.Res Microbiol. 2000 Jul-Aug;151(6):437-43. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2508(00)00172-8. Res Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10961456 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure, Function, and Regulation of LytA: The N-Acetylmuramoyl-l-alanine Amidase Driving the "Suicidal Tendencies" of Streptococcus pneumoniae-A Review.Microorganisms. 2025 Apr 5;13(4):827. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13040827. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40284663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pneumococcal Choline-Binding Proteins Involved in Virulence as Vaccine Candidates.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Feb 20;9(2):181. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9020181. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672701 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae: a Plethora of Temperate Bacteriophages With a Role in Host Genome Rearrangement.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Nov 18;11:775402. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.775402. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34869076 Free PMC article.
-
Recombination in Bacterial Genomes: Evolutionary Trends.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;15(9):568. doi: 10.3390/toxins15090568. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37755994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into the Evolutionary Relationships of LytA Autolysin and Ply Pneumolysin-Like Genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae and Related Streptococci.Genome Biol Evol. 2015 Sep 8;7(9):2747-61. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evv178. Genome Biol Evol. 2015. PMID: 26349755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abedon, S. T. 2009. Phage evolution and ecology. Adv. Appl. Microbiol. 67:1-45. - PubMed
-
- Arbique, J. C., C. Poyart, P. Trieu-Cuot, G. Quesne, M. D. S. Carvalho, A. G. Steigerwalt, R. E. Morey, D. Jackson, R. J. Davidson, and R. R. Facklam. 2004. Accuracy of phenotypic and genotypic testing for identification of Streptococcus pneumoniae and description of Streptococcus pseudopneumoniae sp. nov. J. Clin. Microbiol. 42:4686-4696. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

