Tyrosines 868, 966, and 972 in the kinase domain of JAK2 are autophosphorylated and required for maximal JAK2 kinase activity
- PMID: 20304997
- PMCID: PMC2870937
- DOI: 10.1210/me.2009-0355
Tyrosines 868, 966, and 972 in the kinase domain of JAK2 are autophosphorylated and required for maximal JAK2 kinase activity
Abstract
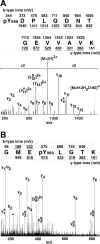
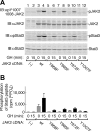
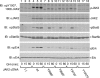
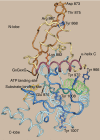
Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) is activated by a majority of cytokine family receptors including receptors for GH, leptin, and erythropoietin. To identify novel JAK2-regulatory and/or -binding sites, we set out to identify autophosphorylation sites in the kinase domain of JAK2. Two-dimensional phosphopeptide mapping of in vitro autophosphorylated JAK2 identified tyrosines 868, 966, and 972 as sites of autophosphorylation. Phosphorylated tyrosines 868 and 972 were also identified by mass spectrometry analysis of JAK2 activated by an erythropoietin-bound chimeric erythropoietin receptor/leptin receptor. Phosphospecific antibodies suggest that the phosphorylation of all three tyrosines increases in response to GH. Compared with wild-type JAK2, which is constitutively active when overexpressed, JAK2 lacking tyrosine 868, 966, or 972 has substantially reduced activity. Coexpression with GH receptor and protein tyrosine phosphatase1B allowed us to investigate GH-dependent activation of these mutated JAK2s in human embryonic kidney 293T cells. All three mutated JAK2s are activated by GH, although to a lesser extent than wild-type JAK2. The three mutated JAK2s also mediate GH activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3), signal transducer and activator of transcription 5b (Stat5b) and ERK1, but at reduced levels. Coexpression with Src-homology 2B1beta (SH2B1beta), like coexpression with GH-bound GH receptor, partially restores the activity of all three JAK2 mutants. Based on these results and the crystal structure of the JAK2 kinase domain, we hypothesize that small changes in the conformation of the regions of JAK2 surrounding tyrosines 868, 966, and 972 due to e.g. phosphorylation, binding to a ligand-bound cytokine receptor, and/or binding to Src-homology 2B1, may be essential for JAK2 to assume a maximally active conformation.
Figures




References
-
- Argetsinger LS, Carter-Su C 1996 Mechanism of signaling by growth hormone receptor. Physiol Rev 76:1089–1107 - PubMed
-
- Smit LS, Meyer DJ, Argetsinger LS, Schwartz J, Carter-Su C 1999 Molecular events in growth hormone-receptor interaction and signaling. In: Kostyo JL, ed. Handbook of physiology. New York: Oxford University Press; 445–480
-
- Marrero MB, Schieffer B, Paxton WG, Heerdt L, Berk BC, Delafontaine P, Bernstein KE 1995 Direct stimulation of Jak/STAT pathway by the angiotensin II AT1 receptor. Nature 375:247–250 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DK56731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK34171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60-DK20572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA046592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA46592/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P60-AR20557/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK056731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK034171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK034171/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK056731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

