Single-batch production of recombinant human polyclonal antibodies
- PMID: 20306237
- PMCID: PMC2881207
- DOI: 10.1007/s12033-010-9270-9
Single-batch production of recombinant human polyclonal antibodies
Abstract
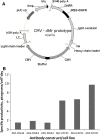
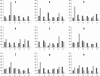
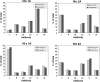
We have previously described the development and implementation of a strategy for production of recombinant polyclonal antibodies (rpAb) in single batches employing CHO cells generated by site-specific integration, the Sympress I technology. The Sympress I technology is implemented at industrial scale, supporting a phase II clinical development program. Production of recombinant proteins by site-specific integration, which is based on incorporation of a single copy of the gene of interest, makes the Sympress I technology best suited to support niche indications. To improve titers while maintaining a cost-efficient, highly reproducible single-batch manufacturing mode, we have evaluated a number of different approaches. The most successful results were obtained using random integration in a new producer cell termed ECHO, a CHO DG44 cell derivative engineered for improved productivity at Symphogen. This new expression process is termed the Sympress II technology. Here we describe proof-of-principle data demonstrating the feasibility of the Sympress II technology for single-batch rpAb manufacturing using two model systems each composed of six target-specific antibodies. The compositional stability and the batch-to-batch reproducibility of rpAb produced by the ECHO cells were at least as good as observed previously using site-specific integration technology. Furthermore, the new process had a significant titer increase.
Figures
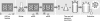
Similar articles
-
CHO cells in biotechnology for production of recombinant proteins: current state and further potential.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012 Feb;93(3):917-30. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3758-5. Epub 2011 Dec 9. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22159888 Review.
-
Production of target-specific recombinant human polyclonal antibodies in mammalian cells.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006 Jun 5;94(2):396-405. doi: 10.1002/bit.20865. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006. PMID: 16596663
-
Recombinant antibody mixtures: production strategies and cost considerations.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012 Oct 15;526(2):139-45. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2012.07.001. Epub 2012 Jul 20. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22820097 Review.
-
Productivity and quality of recombinant proteins produced by stable CHO cell clones can be predicted by transient expression in HEK cells.Mol Biotechnol. 2013 Jun;54(2):497-503. doi: 10.1007/s12033-012-9590-z. Mol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 22915356
-
Benchmarking of commercially available CHO cell culture media for antibody production.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;99(11):4645-57. doi: 10.1007/s00253-015-6514-4. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25846330 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A rational approach to enhancing antibody Fc homodimer formation for robust production of antibody mixture in a single cell line.J Biol Chem. 2017 Oct 27;292(43):17885-17896. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.771188. Epub 2017 Sep 6. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28878018 Free PMC article.
-
Biopharmaceutical benchmarks 2014.Nat Biotechnol. 2014 Oct;32(10):992-1000. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3040. Nat Biotechnol. 2014. PMID: 25299917 No abstract available.
-
Next generation antibody drugs: pursuit of the 'high-hanging fruit'.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018 Mar;17(3):197-223. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.227. Epub 2017 Dec 1. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2018. PMID: 29192287 Review.
-
Fit-for-purpose heterodivalent single-domain antibody for gastrointestinal targeting of toxin B from Clostridium difficile.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5035. doi: 10.1002/pro.5035. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38923049 Free PMC article.
-
Recombinant antibody mixtures; optimization of cell line generation and single-batch manufacturing processes.BMC Proc. 2011 Nov 22;5 Suppl 8(Suppl 8):O2. doi: 10.1186/1753-6561-5-S8-O2. eCollection 2011. BMC Proc. 2011. PMID: 22373259 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Scaradavou A, Woo B, Woloski BMR, Cunningham-Rundles C, Ettinger LJ, Aledort LM, Bussel JB. Intravenous anti-D treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura: Experience in 272 patients. Blood. 1997;89:2689–2700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

