Heme oxygenase-1 gene delivery by Sleeping Beauty inhibits vascular stasis in a murine model of sickle cell disease
- PMID: 20306336
- PMCID: PMC2877767
- DOI: 10.1007/s00109-010-0613-6
Heme oxygenase-1 gene delivery by Sleeping Beauty inhibits vascular stasis in a murine model of sickle cell disease
Abstract
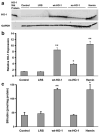
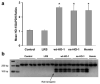
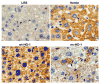
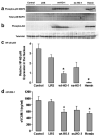
Increases in heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and administration of heme degradation products CO and biliverdin inhibit vascular inflammation and vasoocclusion in mouse models of sickle cell disease (SCD). In this study, an albumin (alb) promoter-driven Sleeping Beauty (SB) transposase plasmid with a wild-type rat hmox-1 (wt-HO-1) transposable element was delivered by hydrodynamic tail vein injections to SCD mice. Eight weeks after injection, SCD mice had three- to five-fold increases in HO-1 activity and protein expression in liver, similar to hemin-treated mice. Immunohistochemistry demonstrated increased perinuclear HO-1 staining in hepatocytes. Messenger RNA transcription of the hmox-1 transgene in liver was confirmed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism (qRT-PCR RFLP) with no detectible transgene expression in other organs. The livers of all HO-1 overexpressing mice had activation of nuclear phospho-p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phospho-Akt, decreased nuclear expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappaB) p65, and decreased soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) in serum. Hypoxia-induced stasis, a characteristic of SCD, but not normal mice, was inhibited in dorsal skin fold chambers in wt-HO-1 SCD mice despite the absence of hmox-1 transgene expression in the skin suggesting distal effects of HO activity on the vasculature. No protective effects were seen in SCD mice injected with nonsense (ns-) rat hmox-1 that encodes carboxy-truncated HO-1 with little or no enzyme activity. We speculate that HO-1 gene delivery to the liver is beneficial in SCD mice by degrading pro-oxidative heme, releasing anti-inflammatory heme degradation products CO and biliverdin/bilirubin into circulation, activating cytoprotective pathways and inhibiting vascular stasis at sites distal to transgene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) method for monitoring highly conserved transgene expression during gene therapy.Transl Res. 2008 Dec;152(6):290-7. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2008.10.005. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Transl Res. 2008. PMID: 19059164 Free PMC article.
-
H-ferritin ferroxidase induces cytoprotective pathways and inhibits microvascular stasis in transgenic sickle mice.Front Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 17;5:79. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00079. eCollection 2014. Front Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24860503 Free PMC article.
-
MP4CO, a pegylated hemoglobin saturated with carbon monoxide, is a modulator of HO-1, inflammation, and vaso-occlusion in transgenic sickle mice.Blood. 2013 Oct 10;122(15):2757-64. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-02-486282. Epub 2013 Aug 1. Blood. 2013. PMID: 23908468 Free PMC article.
-
Patrolling monocytes in sickle cell hemolytic conditions.Transfus Clin Biol. 2019 May;26(2):128-129. doi: 10.1016/j.tracli.2019.02.004. Epub 2019 Feb 22. Transfus Clin Biol. 2019. PMID: 30898432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The heme oxygenase system: its role in liver inflammation.Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2003 Sep;3(3):199-208. doi: 10.2174/1568006033481410. Curr Drug Targets Cardiovasc Haematol Disord. 2003. PMID: 12871038 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatic Overexpression of Hemopexin Inhibits Inflammation and Vascular Stasis in Murine Models of Sickle Cell Disease.Mol Med. 2016 Sep;22:437-451. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2016.00063. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27451971 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of C5a in sickle cell disease.Am J Hematol. 2019 Mar;94(3):327-337. doi: 10.1002/ajh.25384. Epub 2019 Jan 3. Am J Hematol. 2019. PMID: 30569594 Free PMC article.
-
Herb pair Danggui-Honghua: mechanisms underlying blood stasis syndrome by system pharmacology approach.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 11;7:40318. doi: 10.1038/srep40318. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28074863 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical and clinical advances in transposon-based gene therapy.Biosci Rep. 2017 Dec 5;37(6):BSR20160614. doi: 10.1042/BSR20160614. Print 2017 Dec 22. Biosci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29089466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic approaches to limit hemolysis-driven endothelial dysfunction: scavenging free heme to preserve vasculature homeostasis.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:396527. doi: 10.1155/2013/396527. Epub 2013 May 27. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013. PMID: 23781294 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jay U. Methemoglobin—it's not just blue: a concise review. Am J Hematol. 2007;82:134–144. - PubMed
-
- Wagener FA, Eggert A, Boerman OC, Oyen WJ, Verhofstad A, Abraham NG, Adema G, van Kooyk Y, de Witte T, Figdor CG. Heme is a potent inducer of inflammation in mice and is counteracted by heme oxygenase. Blood. 2001;98:1802–1811. - PubMed
-
- Belcher JD, Mahaseth H, Welch TE, Vilback AE, Sonbol KM, Kalambur VS, Bowlin PR, Bischof JC, Hebbel RP, Vercellotti GM. Critical role of endothelial cell activation in hypoxia-induced vasoocclusion in transgenic sickle mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2005;288:H2715–2725. - PubMed
-
- Otterbein LE, Soares MP, Yamashita K, Bach FH. Heme oxygenase-1: unleashing the protective properties of heme. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:449–455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

