Cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases: important roles in the metabolism of naturally occurring sulfur and selenium-containing compounds, xenobiotics and anticancer agents
- PMID: 20306345
- PMCID: PMC2898922
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-010-0552-0
Cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases: important roles in the metabolism of naturally occurring sulfur and selenium-containing compounds, xenobiotics and anticancer agents
Abstract
Cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases are pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-containing enzymes that catalyze β-elimination reactions with cysteine S-conjugates that possess a good leaving group in the β-position. The end products are aminoacrylate and a sulfur-containing fragment. The aminoacrylate tautomerizes and hydrolyzes to pyruvate and ammonia. The mammalian cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases thus far identified are enzymes involved in amino acid metabolism that catalyze β-lyase reactions as non-physiological side reactions. Most are aminotransferases. In some cases the lyase is inactivated by reaction products. The cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases are of much interest to toxicologists because they play an important key role in the bioactivation (toxication) of halogenated alkenes, some of which are produced on an industrial scale and are environmental contaminants. The cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases have been reviewed in this journal previously (Cooper and Pinto in Amino Acids 30:1-15, 2006). Here, we focus on more recent findings regarding: (1) the identification of enzymes associated with high-M(r) cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases in the cytosolic and mitochondrial fractions of rat liver and kidney; (2) the mechanism of syncatalytic inactivation of rat liver mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase by the nephrotoxic β-lyase substrate S-(1,1,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl)-L-cysteine (the cysteine S-conjugate of tetrafluoroethylene); (3) toxicant channeling of reactive fragments from the active site of mitochondrial aspartate aminotransferase to susceptible proteins in the mitochondria; (4) the involvement of cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases in the metabolism/bioactivation of drugs and natural products; and (5) the role of cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases in the metabolism of selenocysteine Se-conjugates. This review emphasizes the fact that the cysteine S-conjugate β-lyases are biologically more important than hitherto appreciated.
Figures

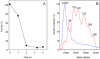


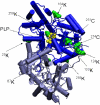

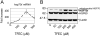

References
-
- Abraham DG, Cooper AJL. Glutamine transaminase K and cysteine S-conjugate β-lyase activity stains. Anal Biochem. 1991;197:421–427. - PubMed
-
- Abraham DG, Cooper AJL. Cloning and expression of a rat kidney cytosolic glutamine transaminase K that has strong sequence homology to kynurenine-pyruvate aminotransferase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1996;335:311–320. - PubMed
-
- Abraham DG, Patel PP, Cooper AJL. Isolation from rat kidney of a high molecular weight cysteine S-conjugate β-lyase with activity toward leukotriene E4. J Biol Chem. 1995a;270:180–188. - PubMed
-
- Abraham DG, Thomas RJ, Cooper AJL. Glutamine transaminase K is not a major cysteine S-conjugate β-lyase of rat kidney mitochondria: Evidence that a high-molecular-weight enzyme fulfills this role. Mol Pharmacol. 1995b;48:855–860. - PubMed
-
- Adams B, Lowpetch K, Thorndycroft F, Whyte SM, Young DW. Stereochemistry of reactions of the inhibitor/substrates L- and D-chloroalanine with β-mercaptoethanol catalysed by L-aspartate aminotransferase and D-amino acid aminotransferase respectively. Org Biomol Med. 2005;3:3357–3364. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

