Uncoupled responses of Smad4-deficient cancer cells to TNFalpha result in secretion of monomeric laminin-gamma2
- PMID: 20307265
- PMCID: PMC2853515
- DOI: 10.1186/1476-4598-9-65
Uncoupled responses of Smad4-deficient cancer cells to TNFalpha result in secretion of monomeric laminin-gamma2
Abstract
Background: Functional loss of the tumor suppressor Smad4 is involved in pancreatic and colorectal carcinogenesis and has been associated with the acquisition of invasiveness. We have previously demonstrated that the heterotrimeric basement membrane protein laminin-332 is a Smad4 target. Namely, Smad4 functions as a positive transcriptional regulator of all three genes encoding laminin-332; its loss is thus implicated in the reduced or discontinuous deposition of the heterotrimeric basement membrane molecule as evident in carcinomas. Uncoupled expression of laminin genes, on the other hand, namely overexpression of the laminin-gamma2 chain is an impressive marker at invasive edges of carcinomas where tumor cells are maximally exposed to signals from stromal cell types like macrophages. As Smad4 is characterized as an integrator of multiple extracellular stimuli in a strongly contextual manner, we asked if loss of Smad4 may also be involved in uncoupled expression of laminin genes in response to altered environmental stimuli. Here, we address Smad4 dependent effects of the prominent inflammatory cytokine TNFalpha on tumor cells.
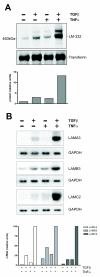
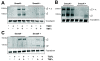
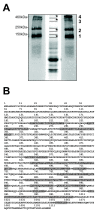
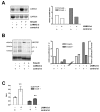
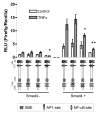
Results: Smad4-reconstituted colon carcinoma cells like adenoma cells respond to TNFalpha with an increased expression of all three chains encoding laminin-332; coincubation with TGFbeta and TNFalpha leads to synergistic induction and to the secretion of large amounts of the heterotrimer. In contrast, in Smad4-deficient cells TNFalpha can induce expression of the gamma2 and beta3 but not the alpha3 chain. Surprisingly, this uncoupled induction of laminin-332 chains in Smad4-negative cells rather than causing intracellular accumulation is followed by the release of gamma2 into the medium, either in a monomeric form or in complexes with as yet unknown proteins. Soluble gamma2 is associated with increased cell migration.
Conclusions: Loss of Smad4 may lead to uncoupled induction of laminin-gamma2 in response to TNFalpha and may therefore represent one of the mechanisms which underlie accumulation of laminin-gamma2 at the invasive margin of a tumor. The finding, that gamma2 is secreted from tumor cells in significant amounts and is associated with increased cell migration may pave the way for further investigation to better understand its functional relevance for tumor progression.
Figures
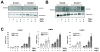
Similar articles
-
Divergent mechanisms underlie Smad4-mediated positive regulation of the three genes encoding the basement membrane component laminin-332 (laminin-5).BMC Cancer. 2008 Jul 29;8:215. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-215. BMC Cancer. 2008. PMID: 18664273 Free PMC article.
-
Basement membrane component laminin-5 is a target of the tumor suppressor Smad4.Oncogene. 2007 Mar 1;26(10):1417-27. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209918. Epub 2006 Sep 4. Oncogene. 2007. PMID: 16953227
-
Co-expression of laminin β3 and γ2 chains and epigenetic inactivation of laminin α3 chain in gastric cancer.Int J Oncol. 2011 Sep;39(3):593-9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2011.1048. Epub 2011 May 20. Int J Oncol. 2011. PMID: 21617852
-
Unique Biological Activity and Potential Role of Monomeric Laminin-γ2 as a Novel Biomarker for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 8;20(1):226. doi: 10.3390/ijms20010226. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30626121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Laminin-5 in epithelial tumour invasion.J Mol Histol. 2004 Mar;35(3):277-86. doi: 10.1023/b:hijo.0000032359.35698.fe. J Mol Histol. 2004. PMID: 15339047 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypoxia promotes histone H3K9 lactylation to enhance LAMC2 transcription in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.iScience. 2024 Jun 5;27(7):110188. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110188. eCollection 2024 Jul 19. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38989468 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of posttranslational modifications in pancreatic carcinogenesis and treatments.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021 Sep;40(3):739-759. doi: 10.1007/s10555-021-09980-4. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2021. PMID: 34342796 Review.
-
Amino-terminal fragments of laminin γ2 chain retract vascular endothelial cells and increase vascular permeability.Cancer Sci. 2014 Feb;105(2):168-75. doi: 10.1111/cas.12323. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Cancer Sci. 2014. PMID: 24238220 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of TNF-α-responsive promoters and enhancers in the intestinal epithelial cell model Caco-2.DNA Res. 2014 Dec;21(6):569-83. doi: 10.1093/dnares/dsu022. Epub 2014 Jul 2. DNA Res. 2014. PMID: 24990076 Free PMC article.
-
Highly sensitive detection of invasive lung cancer cells by novel antibody against amino-terminal domain of laminin γ2 chain.Cancer Sci. 2016 Dec;107(12):1909-1918. doi: 10.1111/cas.13089. Epub 2016 Dec 12. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27685891 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Simon-Assmann P, Bolcato-Bellemin AL, Turck N, Piccinni S, Olsen J, Launay JF, Lefebvre O, Kedinger M. In: Disease Progression and Carcinogenesis in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Johnstone P, editor. London, Kluwer Academic Publishers; 2003. Basement membrane laminins in normal and pathological intestine; pp. 223–239.
-
- Teller IC, Beaulieu JF. Interactions between laminin and epithelial cells in intestinal health and disease. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2001;9:1–18. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

