In silico fragmentation for computer assisted identification of metabolite mass spectra
- PMID: 20307295
- PMCID: PMC2853470
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-11-148
In silico fragmentation for computer assisted identification of metabolite mass spectra
Abstract
Background: Mass spectrometry has become the analytical method of choice in metabolomics research. The identification of unknown compounds is the main bottleneck. In addition to the precursor mass, tandem MS spectra carry informative fragment peaks, but the coverage of spectral libraries of measured reference compounds are far from covering the complete chemical space. Compound libraries such as PubChem or KEGG describe a larger number of compounds, which can be used to compare their in silico fragmentation with spectra of unknown metabolites.
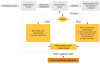
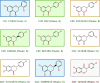
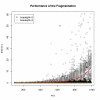
Results: We created the MetFrag suite to obtain a candidate list from compound libraries based on the precursor mass, subsequently ranked by the agreement between measured and in silico fragments. In the evaluation MetFrag was able to rank most of the correct compounds within the top 3 candidates returned by an exact mass query in KEGG. Compared to a previously published study, MetFrag obtained better results than the commercial MassFrontier software. Especially for large compound libraries, the candidates with a good score show a high structural similarity or just different stereochemistry, a subsequent clustering based on chemical distances reduces this redundancy. The in silico fragmentation requires less than a second to process a molecule, and MetFrag performs a search in KEGG or PubChem on average within 30 to 300 seconds, respectively, on an average desktop PC.
Conclusions: We presented a method that is able to identify small molecules from tandem MS measurements, even without spectral reference data or a large set of fragmentation rules. With today's massive general purpose compound libraries we obtain dozens of very similar candidates, which still allows a confident estimate of the correct compound class. Our tool MetFrag improves the identification of unknown substances from tandem MS spectra and delivers better results than comparable commercial software. MetFrag is available through a web application, web services and as java library. The web frontend allows the end-user to analyse single spectra and browse the results, whereas the web service and console application are aimed to perform batch searches and evaluation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MetFusion: integration of compound identification strategies.J Mass Spectrom. 2013 Mar;48(3):291-8. doi: 10.1002/jms.3123. J Mass Spectrom. 2013. PMID: 23494783
-
MetFrag relaunched: incorporating strategies beyond in silico fragmentation.J Cheminform. 2016 Jan 29;8:3. doi: 10.1186/s13321-016-0115-9. eCollection 2016. J Cheminform. 2016. PMID: 26834843 Free PMC article.
-
Annotation of metabolites from gas chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry data using an in silico generated compound database and MetFrag.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2015 Aug 30;29(16):1521-9. doi: 10.1002/rcm.7244. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2015. PMID: 26212167
-
Software Tools and Approaches for Compound Identification of LC-MS/MS Data in Metabolomics.Metabolites. 2018 May 10;8(2):31. doi: 10.3390/metabo8020031. Metabolites. 2018. PMID: 29748461 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Computational mass spectrometry for metabolomics: identification of metabolites and small molecules.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010 Dec;398(7-8):2779-88. doi: 10.1007/s00216-010-4142-5. Epub 2010 Oct 9. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010. PMID: 20936272 Review.
Cited by
-
High-resolution filtering for improved small molecule identification via GC/MS.Anal Chem. 2015 Aug 18;87(16):8328-35. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.5b01503. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Anal Chem. 2015. PMID: 26192401 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell Metabolomics by Mass Spectrometry Imaging.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1280:69-82. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51652-9_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021. PMID: 33791975
-
Development of Database Assisted Structure Identification (DASI) Methods for Nontargeted Metabolomics.Metabolites. 2016 May 31;6(2):17. doi: 10.3390/metabo6020017. Metabolites. 2016. PMID: 27258318 Free PMC article.
-
Biodegradation of sulfamethoxazole by a bacterial consortium of Achromobacter denitrificans PR1 and Leucobacter sp. GP.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Dec;102(23):10299-10314. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9411-9. Epub 2018 Oct 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30294753
-
Metabolic reaction network-based recursive metabolite annotation for untargeted metabolomics.Nat Commun. 2019 Apr 3;10(1):1516. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09550-x. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 30944337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Horai H, Arita M, Nishioka T. Comparison of ESI-MS Spectra in MassBank Database. BioMedical Engineering and Informatics, 2008. BMEI 2008. International Conference on. 2008;2:853–857. full_text.
-
- Smith CA, Maille GO, Want EJ, Qin C, Trauger SA, Brandon TR, Custodio DE, Abagyan R, Siuzdak G. Proceedings of the 9th International Congress of Therapeutic Drug Monitoring and Clinical Toxicology. Vol. 27. Louisville, Kentucky; 2005. METLIN: A Metabolite Mass Spectral Database; pp. 747–751. - PubMed
-
- ACD/MS Fragmenter. http://www.acdlabs.com/products/adh/ms/ms_frag/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

