Peripherally injected CCK-8S activates CART positive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus in rats
- PMID: 20307613
- PMCID: PMC4040251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.03.013
Peripherally injected CCK-8S activates CART positive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus in rats
Abstract
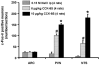
Cholecystokinin (CCK) plays a role in the short-term inhibition of food intake. Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide has been observed in neurons of the paraventricular nucleus (PVN). It has been reported that intracerebroventricular injection of CART peptide inhibits food intake in rodents. The aim of the study was to determine whether intraperitoneally (ip) injected CCK-8S affects neuronal activity of PVN-CART neurons. Ad libitum fed male Sprague-Dawley rats received 6 or 10 microg/kg CCK-8S or 0.15M NaCl ip (n=4/group). The number of c-Fos-immunoreactive neurons was determined in the PVN, arcuate nucleus (ARC), and the nucleus of the solitary tract (NTS). CCK-8S dose-dependently increased the number of c-Fos-immunoreactive neurons in the PVN (mean+/-SEM: 102+/-6 vs. 150+/-5 neurons/section, p<0.05) and compared to vehicle treated rats (18+/-7, p<0.05 vs. 6 and 10 microg/kg CCK-8S). CCK-8S at both doses induced an increase in the number of c-Fos-immunoreactive neurons in the NTS (65+/-13, p<0.05, and 182+/-16, p<0.05). No effect on the number of c-Fos neurons was observed in the ARC. Immunostaining for CART and c-Fos revealed a dose-dependent increase of activated CART neurons (19+/-3 vs. 29+/-7; p<0.05), only few activated CART neuron were observed in the vehicle group (1+/-0). The present observation shows that CCK-8S injected ip induces an increase in neuronal activity in PVN-CART neurons and suggests that CART neurons in the PVN may play a role in the mediation of peripheral CCK-8S's anorexigenic effects.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

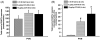



Similar articles
-
Sulfated cholecystokinin-8 activates phospho-mTOR immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus in rats.Peptides. 2011 Jan;32(1):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.09.025. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 20933028 Free PMC article.
-
CCK-8S activates c-Fos in a dose-dependent manner in nesfatin-1 immunoreactive neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and in the nucleus of the solitary tract of the brainstem.Regul Pept. 2009 Oct 9;157(1-3):84-91. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2009.06.009. Epub 2009 Jun 21. Regul Pept. 2009. PMID: 19540880
-
Peripheral injection of CCK-8S induces Fos expression in the dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus in rats.Brain Res. 2006 Oct 30;1117(1):109-17. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.092. Epub 2006 Sep 26. Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 17005163
-
Peripheral injected cholecystokinin-8S modulates the concentration of serotonin in nerve fibers of the rat brainstem.Peptides. 2014 Sep;59:25-33. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2014.07.003. Epub 2014 Jul 10. Peptides. 2014. PMID: 25017242
-
Peripheral injection of bombesin induces c-Fos in NUCB2/nesfatin-1 neurons.Brain Res. 2016 Oct 1;1648(Pt A):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2016.07.006. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27396908
Cited by
-
Insulin Activates Vagal Afferent Neurons Including those Innervating Pancreas via Insulin Cascade and Ca(2+) Influx: Its Dysfunction in IRS2-KO Mice with Hyperphagic Obesity.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 26;8(6):e67198. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067198. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23840624 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic expression of Irx3 and Irx5 in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus contributes to defects in Sim1 haploinsufficiency.Sci Adv. 2021 Oct 29;7(44):eabh4503. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abh4503. Epub 2021 Oct 27. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34705510 Free PMC article.
-
Cholecystokinin system is involved in the anorexigenic effect of peripherally applied palmitoylated prolactin-releasing peptide in fasted mice.Physiol Res. 2021 Aug 31;70(4):579-590. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.934694. Epub 2021 Jun 1. Physiol Res. 2021. PMID: 34062082 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfated cholecystokinin-8 activates phospho-mTOR immunoreactive neurons of the paraventricular nucleus in rats.Peptides. 2011 Jan;32(1):65-70. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2010.09.025. Epub 2010 Oct 7. Peptides. 2011. PMID: 20933028 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript is the neurotransmitter regulating the action of cholecystokinin and leptin on short-term satiety in rats.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012 Nov 1;303(9):G1042-51. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00231.2012. Epub 2012 Aug 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2012. Retraction in: Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2023 Feb 1;324(2):G157. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00231.2012_RET. PMID: 22936273 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Asakawa A, Inui A, Yuzuriha H, Nagata T, Kaga T, Ueno N, et al. Cocaine-amphetamine-regulated transcript influences energy metabolism, anxiety and gastric emptying in mice. Horm Metab Res. 2001;33:554–8. - PubMed
-
- Balkan B, Koylu E, Pogun S, Kuhar MJ. Effects of adrenalectomy on CART expression in the rat arcuate nucleus. Synapse. 2003;50:14–9. - PubMed
-
- Buffa R, Solcia E, Go VL. Immunohistochemical identification of the cholecystokinin cell in the intestinal mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1976;70:528–32. - PubMed
-
- Calogero AE, Nicolosi AM, Moncada ML, Coniglione F, Vicari E, Polosa P, et al. Effects of cholecystokinin octapeptide on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis function and on vasopressin, prolactin and growth hormone release in humans. Neuroendocrinology. 1993;58:71–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

