Mast cell-derived prostaglandin D2 controls hyaluronan synthesis in human orbital fibroblasts via DP1 activation: implications for thyroid eye disease
- PMID: 20308056
- PMCID: PMC2871447
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M109.074534
Mast cell-derived prostaglandin D2 controls hyaluronan synthesis in human orbital fibroblasts via DP1 activation: implications for thyroid eye disease
Abstract
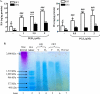
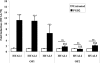
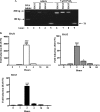
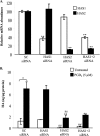
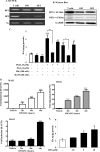
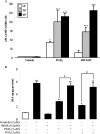
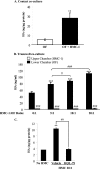
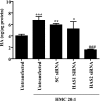
Thyroid eye disease (TED) is a debilitating disorder characterized by the accumulation of adipocytes and hyaluronan (HA). Production of HA by fibroblasts leads to remarkable increases in tissue volume and to the anterior displacement of the eyes. Prostaglandin D(2) (PGD(2)), mainly produced by mast cells, promotes orbital fibroblast adipogenesis. The mechanism by which PGD(2) influences orbital fibroblasts and their synthesis of HA is poorly understood. We report here that mast cell-derived PGD(2) is a key factor that promotes HA biosynthesis by orbital fibroblasts. Primary orbital fibroblasts from TED patients were isolated and used to test the effects of PGD(2), prostaglandin J(2), as well as prostaglandin D receptor (DP) agonists and antagonists on HA synthesis. The expression of HA synthase (HAS), hyaluronidase, DP1, and DP2 mRNA levels was assessed by PCR. Small interfering RNAs against HAS1 or HAS2 were used to assess the importance of HAS isoforms on HA production. Treatment of human orbital fibroblasts with PGD(2) and PGJ(2) increased HA synthesis and HAS mRNA. HAS2 was the dominant isoform responsible for HA production by PGD(2). The effect of PGD(2) on HA production was mimicked by the selective DP1 agonist BW245C. The DP1 antagonist MK-0524 completely blocked PGD(2)-induced HA synthesis. Human mast cells (HMC-1) produced PGD(2). Co-culture of HMC-1 cells with orbital fibroblasts induced HA production and inhibition of mast cell-derived PGD(2) prevented HA synthesis. Mast cell-derived PGD(2) increased HA production via activation of DP1. Selectively targeting the production of PGD(2) and/or activation of DP1 may prevent pathological changes associated with TED.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyclosporin A inhibits PDGF-BB induced hyaluronan synthesis in orbital fibroblasts.Chem Biol Interact. 2024 Jun 1;396:111045. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2024.111045. Epub 2024 May 9. Chem Biol Interact. 2024. PMID: 38729283
-
Prostaglandin D2 mediates neuronal protection via the DP1 receptor.J Neurochem. 2005 Feb;92(3):477-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02870.x. J Neurochem. 2005. PMID: 15659218
-
HMC-1 mast cells activate human orbital fibroblasts in coculture: evidence for up-regulation of prostaglandin E2 and hyaluronan synthesis.Endocrinology. 1999 Aug;140(8):3518-25. doi: 10.1210/endo.140.8.6881. Endocrinology. 1999. PMID: 10433207
-
Prostaglandin D2 receptor antagonists in allergic disorders: safety, efficacy, and future perspectives.Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019 Jan;28(1):73-84. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1555237. Epub 2018 Dec 7. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019. PMID: 30513028 Review.
-
Unique properties of orbital connective tissue underlie its involvement in Graves' disease.Minerva Endocrinol. 2003 Sep;28(3):213-22. Minerva Endocrinol. 2003. PMID: 14605603 Review.
Cited by
-
Carcinogenesis: the cancer cell-mast cell connection.Inflamm Res. 2019 Feb;68(2):103-116. doi: 10.1007/s00011-018-1201-4. Epub 2018 Nov 20. Inflamm Res. 2019. PMID: 30460391 Review.
-
Thinking inside the box: Current insights into targeting orbital tissue remodeling and inflammation in thyroid eye disease.Surv Ophthalmol. 2022 May-Jun;67(3):858-874. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2021.08.010. Epub 2021 Sep 4. Surv Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 34487739 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunological Aspects of Graves' Ophthalmopathy.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Nov 12;2019:7453260. doi: 10.1155/2019/7453260. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31781640 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor pathway controls matrix metalloproteinase-1 and collagen levels in human orbital fibroblasts.Sci Rep. 2020 May 21;10(1):8477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65414-1. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32439897 Free PMC article.
-
Adelmidrol, in combination with hyaluronic acid, displays increased anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects against monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in rats.Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Dec 12;18(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1189-5. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27955699 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

