Transposable elements in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 20308097
- PMCID: PMC2871824
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2009.0318
Transposable elements in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
Transposable elements (TEs) are families of small DNA sequences found in the genomes of virtually all organisms. The sequences typically encode essential components for the replicative transposition sequences of that TE family. Thus, TEs are simply genomic parasites that inflict detrimental mutations on the fitness of their hosts. Several models have been proposed for the containment of TE copy number in outbreeding host populations such as Drosophila. Surveys of the TEs in genomes from natural populations of Drosophila have played a central role in the investigation of TE dynamics. The early surveys indicated that a typical TE insertion is rare in a population, which has been interpreted as evidence that each TE is selected against. The proposed mechanisms of this natural selection are reviewed here. Subsequent and more targeted surveys identify heterogeneity among types of TEs and also highlight the large role of homologous and possibly ectopic crossing over in the dynamics of the Drosophila TEs. The recent discovery of germline-specific RNA interference via the piwi-interacting RNA pathway opens yet another interesting mechanism that may be critical in containing the copy number of TEs in natural populations of Drosophila. The expected flood of Drosophila population genomics is expected to rapidly advance understanding of the dynamics of TEs.
Figures
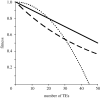
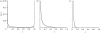
 . These three figures depict the impact of β as population size, Ne, goes from 104 (β = 0.4) to 105 (β = 4) and then to 106 (β = 40). The probability a TE insertion will occur at intermediate or high frequencies increases dramatically. Other assumed parameters are u = 10−5, T = 4 × 104 and
. These three figures depict the impact of β as population size, Ne, goes from 104 (β = 0.4) to 105 (β = 4) and then to 106 (β = 40). The probability a TE insertion will occur at intermediate or high frequencies increases dramatically. Other assumed parameters are u = 10−5, T = 4 × 104 and  . (a) α = 0.0005, β = 0.4; (b) α = 0.005, β = 4 and (c) α = 0.05, β = 40.
. (a) α = 0.0005, β = 0.4; (b) α = 0.005, β = 4 and (c) α = 0.05, β = 40.
Similar articles
-
Analysis of piRNA-mediated silencing of active TEs in Drosophila melanogaster suggests limits on the evolution of host genome defense.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Aug;30(8):1816-29. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst081. Epub 2013 Apr 26. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23625890 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of Transposable Elements by piRNAs in Drosophila: An Evolutionary Perspective.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017 Jun;15(3):164-176. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2017.01.006. Epub 2017 Jun 8. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 28602845 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The evolutionary arms race between transposable elements and piRNAs in Drosophila melanogaster.BMC Evol Biol. 2020 Jan 28;20(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s12862-020-1580-3. BMC Evol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31992188 Free PMC article.
-
QTL mapping of natural variation reveals that the developmental regulator bruno reduces tolerance to P-element transposition in the Drosophila female germline.PLoS Biol. 2018 Oct 30;16(10):e2006040. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006040. eCollection 2018 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2018. PMID: 30376574 Free PMC article.
-
Maintenance of transposable element copy number in natural populations of Drosophila melanogaster and D. simulans.Genetica. 1997;100(1-3):161-6. Genetica. 1997. PMID: 9440269 Review.
Cited by
-
The dawn of active genetics.Bioessays. 2016 Jan;38(1):50-63. doi: 10.1002/bies.201500102. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 26660392 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequencing of pooled DNA samples (Pool-Seq) uncovers complex dynamics of transposable element insertions in Drosophila melanogaster.PLoS Genet. 2012 Jan;8(1):e1002487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002487. Epub 2012 Jan 26. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 22291611 Free PMC article.
-
Blessing or curse: how the epigenetic resolution of host-transposable element conflicts shapes their evolutionary dynamics.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Apr 10;291(2020):20232775. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.2775. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38593848 Free PMC article.
-
Dispersion Profiles and Gene Associations of Repetitive DNAs in the Euchromatin of the Beetle Tribolium castaneum.G3 (Bethesda). 2018 Mar 2;8(3):875-886. doi: 10.1534/g3.117.300267. G3 (Bethesda). 2018. PMID: 29311112 Free PMC article.
-
Telomeric TART elements target the piRNA machinery in Drosophila.PLoS Biol. 2020 Dec 21;18(12):e3000689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000689. eCollection 2020 Dec. PLoS Biol. 2020. PMID: 33347429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aminetzach Y. T., Macpherson J. M., Petrov D. A.2005Pesticide resistance via transposition-mediated adaptive gene truncation in Drosophila. Science 309, 764–767 (doi:10.1126/science.1112699) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aravin A. A., Hannon G. J., Brennecke J.2007The Piwi-piRNA pathway provides an adaptive defense in the transposon arms race. Science 318, 761–764 (doi:10.1126/science.1146484) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartolome C., Maside X.2004The lack of recombination drives the fixation of transposable elements on the fourth chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Genet. Res. 83, 91–100 (doi:10.1017/S0016672304006755) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartolome C., Maside X., Charlesworth B.2002On the abundance and distribution of transposable elements in the genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Biol. Evol. 19, 926–937 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

