Oxytocin, dopamine, and the amygdala: a neurofunctional model of social cognitive deficits in schizophrenia
- PMID: 20308198
- PMCID: PMC3160224
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbq015
Oxytocin, dopamine, and the amygdala: a neurofunctional model of social cognitive deficits in schizophrenia
Abstract
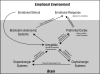
Until recently, the social cognitive impairment in schizophrenia has been underappreciated and remains essentially untreated. Deficits in emotional processing, social perception and knowledge, theory of mind, and attributional bias may contribute to functional social cognitive impairments in schizophrenia. The amygdala has been implicated as a key component of social cognitive circuitry in both animal and human studies. In addition, structural and functional studies of schizophrenia reproducibly demonstrate abnormalities in the amygdala and dopaminergic signaling. Finally, the neurohormone oxytocin plays an important role in multiple social behaviors in several mammals, including humans. We propose a model of social cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia and discuss its therapeutic implications. The model comprises abnormalities in oxytocinergic and dopaminergic signaling in the amygdala that result in impaired emotional salience processing with consequent social cognitive deficits.
Figures
References
-
- Sergi MJ, Green MF, Widmark C, et al. Social cognition [corrected] and neurocognition: effects of risperidone, olanzapine, and haloperidol. Am J Psychiatry. 2007;164:1585–1592. - PubMed
-
- Harvey PD, Patterson TL, Potter LS, Zhong K, Brecher M. Improvement in social competence with short-term atypical antipsychotic treatment: a randomized, double-blind comparison of quetiapine versus risperidone for social competence, social cognition, and neuropsychological functioning. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1918–1925. - PubMed
-
- Horan W, Kern RS, Green M, Penn DL. Social cognition training for individuals with schizophrenia: emerging evidence. Am J Psychiatr Rehabil. 2008;11:205–252.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

