Zebrafish as a model host for Candida albicans infection
- PMID: 20308295
- PMCID: PMC2876552
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01293-09
Zebrafish as a model host for Candida albicans infection
Abstract
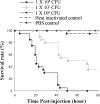
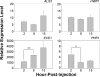
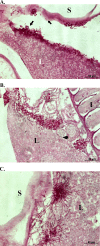
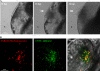
In this work, the zebrafish model organism was developed to obtain a minivertebrate host system for a Candida albicans infection study. We demonstrated that C. albicans can colonize and invade zebrafish at multiple anatomical sites and kill the fish in a dose-dependent manner. Inside zebrafish, we monitored the progression of the C. albicans yeast-to-hypha transition by tracking morphogenesis, and we monitored the corresponding gene expression of the pathogen and the early host immune response. We performed a zebrafish survival assay with different C. albicans strains (SC5314, ATCC 10231, an hgc1 mutant, and a cph1/efg1 double mutant) to determine each strain's virulence, and the results were similar to findings reported in previous mouse model studies. Finally, using zebrafish embryos, we monitored C. albicans infection and visualized the interaction between pathogen and host myelomonocytic cells in vivo. Taken together, the results of this work demonstrate that zebrafish can be a useful host model to study C. albicans pathogenesis, and they highlight the advantages of using the zebrafish model in future invasive fungal research.
Figures







References
-
- Alarco, A. M., A. Marcil, J. Chen, B. Suter, D. Thomas, and M. Whiteway. 2004. Immune-deficient Drosophila melanogaster: a model for the innate immune response to human fungal pathogens. J. Immunol. 172:5622-5628. - PubMed
-
- Berman, J., and P. E. Sudbery. 2002. Candida albicans: a molecular revolution built on lessons from budding yeast. Nat. Rev. Genet. 3:918-930. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

